While some people love the sun-kissed glow, others may find it unsightly and wish to remove it. Tanning occurs when the skin produces melanin, a pigment that protects the skin from UV radiation. However, excessive exposure to the sun can cause an uneven and dark tan, which can take a long time to fade away. In this blog, we will discuss how to remove tan from hands and face.
What is tanning?
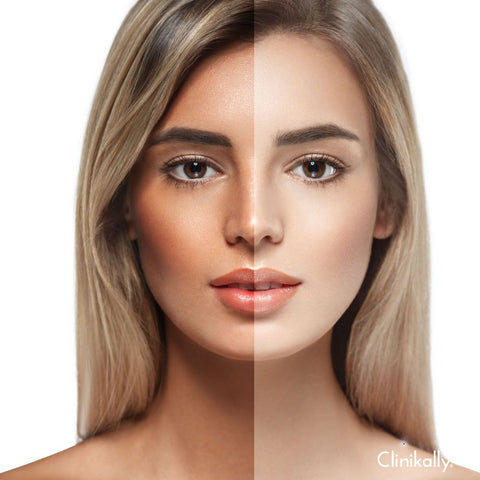

Tanning is a natural process that occurs when the skin is exposed to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. When the skin is exposed to UV rays, the body produces more melanin to protect itself from the harmful effects of the sun. This results in a darker skin tone, which is known as tanning. However, too much exposure to the sun without adequate sun protection can cause an uneven and dark tan that may take a long time to fade away.
Effects of UV radiation on skin pigmentation

UV radiation has a variety of effects on skin pigmentation, both short and long term. Here are some of the main effects:
-
Immediate Tanning: When exposed to UV radiation, particularly UVB rays, the skin produces melanin, the pigment that determines skin colour. This immediate tanning effect is the skin's natural defence mechanism against UV damage, protecting deeper layers from further harm.
-
Increased Pigmentation: Prolonged or repeated UV exposure can cause an increase in skin pigmentation, resulting in darkening of the skin. This can appear as freckles, sunspots, or a more widespread darkening of the skin, known as hyperpigmentation.
-
Sunburn: Overexposure to UV radiation can result in sunburn, which is characterised by redness, discomfort, inflammation, and skin peeling. Sunburn indicates acute damage to skin cells and can have long-term implications such as premature ageing and an increased risk of skin cancer.
-
Photoaging: UV radiation contributes significantly to premature skin ageing, also known as photoaging. Chronic exposure to UV radiation accelerates the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, sagging, and a leathery texture.
-
Melasma Development: UV radiation can exacerbate or cause the development of melasma, a skin condition characterised by hyperpigmented patches on the skin, most commonly on the face. Melasma is often associated with hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or hormonal contraceptives, and UV exposure can worsen existing pigmentation.
-
Risk of Skin Cancer: The most serious long-term impact of UV radiation on skin pigmentation is an increased risk of skin cancer. UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can result in the development of skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Environmental factors contributing to tanning

Tanning are caused by a variety of environmental factors, both natural and artificial. These variables influence the skin's reaction to ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure and melanin production. Here are some important environmental factors:
-
Sunlight is the primary source of UV radiation, which causes melanocytes in the skin to produce melanin. When the skin is exposed to UVB rays, melanin production increases, leading to tanning. UVA rays also contribute to tanning by oxidizing existing melanin in the skin, resulting in a darker pigment.
-
Tanning can vary depending on your geographical location and altitude. Areas near the equator experience higher levels of UV radiation throughout the year, resulting in more intense and frequent tanning. Furthermore, higher altitudes cause more UV exposure due to the thinner atmosphere, potentially leading to more significant tanning effects.
-
Tanning is more common during the summer months, when UV radiation levels are high. In regions with distinct seasons, tanning may be more noticeable in the summer and less so in the winter, when UV radiation is reduced.
-
UV radiation intensity varies throughout the day, peaking between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Tanning is more common during peak hours, when UV radiation levels are highest.
-
Depletion of the ozone layer, especially near the poles, can lead to increased UV radiation reaching the Earth's surface. This can increase the risk of sunburn and tanning, as well as cause long-term skin damage and skin cancer.
-
Sand, water, snow, and pavement can all reflect UV radiation, causing more exposure and increasing the likelihood of tanning. This phenomenon, known as "indirect" or "reflected" UV radiation, can happen even in shaded areas.
-
Tanning beds and sunlamps use artificial UV radiation, primarily UVA and UVB rays, to simulate sunlight exposure. These devices can cause significant tanning and are linked to an increased risk of skin cancer, premature ageing, and other skin damage.
The role of melanin in the tanning process

Melanin is important in tanning because it serves as the skin's natural defence mechanism against UV radiation damage. Melanin is a pigment produced by melanocytes, which are specialised cells in the skin's epidermis. Here's how melanin helps the tanning process:
-
UV Protection: When exposed to UV radiation from sunlight, melanocytes produce melanin as a protective mechanism. Melanin absorbs UV radiation and converts it into heat, which helps to protect DNA in skin cells. This process lowers the risk of sunburn, skin cancer, and other UV-induced skin damage.
-
Melanocyte Stimulation: UV radiation, particularly UVB rays, stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin. This increased melanin production causes the skin to darken, a process known as tanning. The darker pigmentation protects against UV radiation by absorbing and scattering the incoming rays.
-
Melanin Types: The skin contains two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is responsible for brown and black pigmentation and offers superior UV protection. In contrast, pheomelanin produces red and yellow pigments and is less effective at absorbing UV radiation.
-
Skin Distribution: Melanin is not evenly distributed throughout the skin, with higher concentrations found in specific regions like the hair follicles and epidermis. Melanocytes transport melanin to keratinocytes, nearby skin cells, where it envelops the nucleus in a protective layer.
-
Genetic Factors: Skin type, ethnicity, and individual differences in melanin-producing genes all influence the quantity and kind of melanin produced in the skin. People with darker skin tones produce more melanin and have better natural UV protection than those with lighter skin tones.
-
Adaptation to UV Exposure: After repeated UV exposure, the skin undergoes adaptive changes that increase melanin production and provide better UV protection. This adaptive response is commonly characterised by a gradual darkening of the skin, known as a tan, which reduces the risk of sunburn and UV-induced damage over time.
How to remove tan from hands and face

There are several ways to remove tan from hands and faces, including tan removal treatments, home remedies, and skin lightening products. However, it is essential to choose the right method that suits your skin type and condition. It is best to speak to a dermatologist for personalized treatment based on your skin type. You can consult a dermatologist online hassle free and get expert care and personalized recommendations delivered directly. Here are some effective ways to remove tan from hands and face:
Tan removal treatments:
-
Chemical peels: A chemical peel is a treatment that involves applying a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the top layer of dead skin cells. This helps to remove the tanned layer and reveal a new, fresh layer of skin. Chemical peels can be done at a dermatologist's office or at home, but it is important to follow the instructions carefully.
-
Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive treatment that uses a device to exfoliate the skin's top layer. This helps to remove the tanned layer and reveal a new, fresh layer of skin. Microdermabrasion can be done at a dermatologist's office or at home, but it is important to follow the instructions carefully.
-
Laser treatment: Laser treatment is a non-invasive treatment that uses a laser to remove the tanned layer from the skin. This helps to reveal a new, fresh layer of skin. Laser treatment can be done at a dermatologist's office, but it may require multiple sessions to achieve the desired results.
Home remedies to remove tan from hands face:
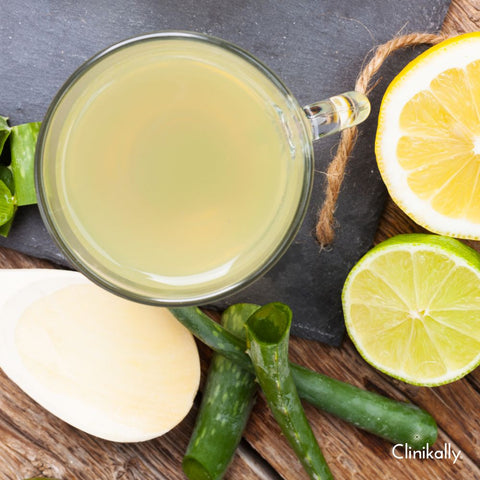

Home remedies can help remove tan from the hands and face by giving natural and mild methods to reduce dark spots, even out skin tone, and restore shine to the skin. Here are some home cures you should consider:
-
Lemon juice: Lemon juice is a natural bleaching agent that can help to remove tan from the skin. Apply fresh lemon juice to the tanned area and leave it for 10-15 minutes. Rinse with water and repeat this process every day for best results.
-
Aloe vera: Aloe vera is a natural moisturiser that can help to soothe and lighten the skin. Apply aloe vera gel to the tanned area and leave it for 15-20 minutes. Rinse with water and repeat this process every day for best results.
-
Tomato: Tomato is a natural bleaching agent that can help to remove tan from the skin. Apply tomato juice to the tanned area and leave it for 10-15 minutes. Rinse with water and repeat this process every day for best results.
Skin lightening products:

Skin lightening products are topical formulations that aim to lighten or minimise the appearance of hyperpigmentation, dark patches, and uneven skin tone. These products usually include active chemicals that reduce melanin synthesis, promote exfoliation, and brighten the face. Here are some prevalent forms of skin lightening products and their main ingredients.
-
Hydroquinone: Hydroquinone is a skin lightening agent that can help to remove the tanned layer from the skin. It is available in various concentrations and can be used under the guidance of a dermatologist.
-
Kojic acid: Kojic acid is a natural skin lightening agent that can help to remove the tanned layer from the skin. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin, which helps to lighten the skin. Kojic acid is available in various forms, such as creams and serums, and can be used under the guidance of a dermatologist.
-
Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a natural antioxidant that can help to lighten the skin and reduce the appearance of tan. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin and promoting collagen production. Vitamin C is available in various forms, such as creams and serums, and can be used under the guidance of a dermatologist.
Preventive measures against tanning

Preventive tanning measures are critical for protecting the skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation and lowering the risk of sunburn, premature ageing, and skin cancer. Here are some important preventive measures to reduce tanning.
-
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 30 or higher to all exposed skin areas before going outside. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating. Choose a sunscreen that protects against UVA and UVB rays.
-
Whenever possible, seek shade during peak sunlight hours, which are typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Shade can protect against direct UV radiation, lowering the risk of sunburn and tanning.
-
To protect your skin and eyes from UV radiation, wear lightweight, long-sleeved shirts and pants, wide-brimmed hats and UV-protected sunglasses. Dark-colored, tightly woven fabrics provide more protection than light-colored, loose-woven clothing.
-
Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps, which emit harmful UV radiation and raise the risk of skin cancer, premature ageing, and other skin damage. To achieve a sun-kissed glow, use safer alternatives like self-tanning lotions or spray tans.
-
Reduce your exposure to UV radiation by limiting your outdoor activities, especially during peak sun hours. Plan outdoor activities for the early morning or late afternoon, when UV levels are lower.
-
Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, especially when spending time outside in hot, sunny weather. Proper hydration promotes skin health and lowers the risk of dehydration and sun-related illnesses.
-
Check the UV index before going outside to determine the intensity of UV radiation and take necessary precautions. Avoid participating in outdoor activities when the UV index is high or extreme.
-
Take extra precautions to protect children and infants from UV radiation because their skin is more susceptible to sun damage. Keep infants under six months old out of direct sunlight and dressed in lightweight, protective clothing and hats.
-
Perform regular self-examinations of your skin to check for changes in moles, freckles, or other lesions. Report any new or suspicious growths to a healthcare professional for examination.
-
Educate family, friends, and community members about sun safety and how to avoid tanning and UV radiation exposure. Encourage others to practise sun-safety and protect their skin from sun damage.
By following these preventive measures, individuals can help reduce tanning, protect their skin from UV radiation, and maintain skin health and vitality for years to come.
Importance of sunscreen in preventing tanning

Sunscreen is essential for preventing tanning by shielding the skin from the sun's harmful UV radiation. There are several reasons why sunscreen is important in preventing tanning.
-
Blocks UV Radiation: Sunscreen contains active ingredients that act as a barrier to UV radiation from the sun. It helps to block UVA and UVB rays, which cause tanning, sunburn, premature ageing, and skin cancer.
-
Prevents Sunburn: Sunburn is a visible indicator of UV radiation damage to the skin, and sunscreen helps avoid it. Individuals who use sunscreen regularly can reduce their risk of sunburn and the immediate darkening of their skin due to tanning.
-
Reduces Skin Damage: Prolonged or repeated UV exposure can cause long-term skin damage, such as premature ageing, wrinkles, sunspots, and other signs of photodamage. Sunscreen reduces the cumulative effects of UV exposure and protects the skin from permanent damage.
-
Minimises Hyperpigmentation: Melasma, freckles, and sunspots are examples of hyperpigmentation that can be caused by UV-induced melanin production. Sunscreen can help prevent or minimise hyperpigmentation. Sunscreen helps maintain more even skin tone and lessens the appearance of pre-existing pigmentation by blocking UV radiation.
-
Reduces Skin Cancer Risk: UV radiation is a well-known carcinogen and a significant contributor to the development of skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and melanoma. By shielding the skin from UV-induced DNA damage, regular use of sunscreen can dramatically lower the risk of developing skin cancer.
-
Preserves Skin Health: Sunscreen helps preserve the overall health and integrity of the skin by preventing UV-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune suppression. By maintaining skin health, sunscreen contributes to a more youthful appearance and reduces the risk of skin diseases and disorders.
-
Supports Anti-Aging Efforts: Sunscreen is a crucial part of any skincare regimen designed to combat the signs of ageing. By protecting the skin from UV radiation, sunscreen helps prevent premature aging, including fine lines, wrinkles, sagging, and loss of elasticity, allowing individuals to maintain a more youthful and radiant complexion.
-
Sun-Safety Behaviour: Including sunscreen in daily skincare routines encourages people to take proactive steps to protect their skin from UV rays. By raising awareness about the importance of sunscreen, individuals can reduce their overall sun exposure and minimize the risk of tanning and sun-related damage.
Protective clothing and accessories for sun exposure

Protective clothing and accessories are necessary to limit sun exposure and reduce the risk of sunburn, tanning, premature ageing, and skin cancer. Here are some examples of sun-protective clothing and accessories.
-
Wear wide-brimmed hats that provide shade for the face, neck, and ears. Choose hats with brims that are at least 3 inches wide to effectively block sunlight. Hats made of tightly woven fabrics provide better sun protection.
-
Choose sunglasses with 100% UV protection to protect your eyes from harmful UV radiation. Look for UV400-labeled sunglasses that protect against both UVA and UVB rays. Wrap-around styles provide extra coverage and protection to the delicate skin around the eyes.
-
Choose clothing with a high Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) rating to block UV radiation. UPF clothing is specifically designed to provide sun protection and may include features such as tighter weaves, UV-absorbing fabrics, and chemical treatments that block or reflect UV rays.
-
To protect your arms and legs from the sun, wear lightweight, long-sleeved shirts and trousers made of tightly woven fabrics. Darker-colored clothing offers better sun protection than lighter-colored clothing.
-
Wear UPF-rated swimwear to protect your skin while swimming or doing other water activities. Look for swim shirts, rash guards, and swim leggings made of UV-protective fabrics to cover more skin and limit sun exposure.
-
Consider wearing sun sleeves or gloves made of UPF fabric to protect your arms and hands from sun damage. Sun sleeves are lightweight, breathable sleeves that can be worn alone or underneath clothing to provide additional sun protection.
-
Neck gaiters and buffs can be worn around the neck, face, and head to provide extra sun protection. Look for neck gaiters made of UPF fabric with moisture-wicking properties for outdoor comfort and sun protection.
-
Sun umbrellas or parasols can be used to provide shade and protect the skin from direct sunlight at outdoor events, picnics, and beach outings. Portable, lightweight umbrellas are ideal for travel and offer on-the-go sun protection.
-
Sun hats with neck flaps or built-in neck covers provide additional sun protection for the neck and upper back. These hats provide extra protection against sunburn and heat-related issues.
-
Look for moisture-wicking cooling towels, hats, and neck wraps to help regulate body temperature and keep skin cool in hot weather.
By incorporating these protective clothing and accessories into your sun safety routine, you can reduce sun exposure, lower your risk of sun damage, and keep your skin healthy for years. Remember to combine these measures with other sun safety practices, such as seeking shade, wearing sunscreen, and avoiding peak sun hours, for comprehensive sun protection.
Seeking shade during peak sun hours

Seeking shade during peak sunlight hours is an important sun safety practice for limiting sun exposure and lowering the risk of sunburn, tanning, and skin damage. Peak sun hours are typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the sun's UV radiation is most intense. Here are some tips for finding shade during peak sunlight hours:
-
Plan Outdoor Activities Wisely: Whenever possible, schedule outdoor activities in the morning or late afternoon to avoid the peak sun hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. Plan indoor activities or seek shade during the midday to reduce sun exposure.
-
Use Natural Shade: To protect yourself from direct sunlight, seek out natural sources of shade such as trees, umbrellas, canopies, awnings, and buildings. Position yourself under a tree or near a shaded area to block UV radiation and stay cool.
-
Bring Portable Shade: Bring portable shade solutions like beach umbrellas, pop-up tents, sun shelters, or portable awnings to provide shade wherever you go. These lightweight and collapsible options are ideal for outdoor activities such as picnics, beach trips, and events.
-
Seek Covered Areas: Look for outdoor venues with covered or shaded areas, such as parks with pavilions, outdoor cafes with umbrellas, or outdoor seating areas with awnings. Take advantage of these shaded areas to enjoy outdoor activities while limiting your sun exposure.
-
Create Your Shade: If natural or portable shade options are unavailable, make your shade with umbrellas, hats, parasols, sun hats with wide brims, or beach tents. Position these items to block direct sunlight and provide shade for you and others.
-
Stay in the Shadow: Position yourself in the shadow of a building, structure, or object that blocks the sun's light. Seek out areas where you can find consistent shade throughout the day, such as the shady side of a building or a covered patio.
-
Rotate with the Sun: As the sun moves throughout the day, shift your position to remain in the shade and avoid direct sunlight exposure. To stay protected from the sun's rays, move your shade-providing items or adjust your seating.
-
Use Shade Accessories: To add extra shade and shield the eyes, face, neck, and ears from UV rays, put on wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses with UV protection. For added sun protection, think about dressing in airy, long-sleeved garments made of breathable materials.
You can lower your risk of sunburn, tanning, and skin damage while enjoying outdoor activities by seeking shade during peak sun hours and taking proactive steps to reduce sun exposure. Remember to combine shade-seeking with other sun safety practices, such as wearing sunscreen, staying hydrated, and wearing protective clothing, for comprehensive sun protection.
Professional tan removal treatments
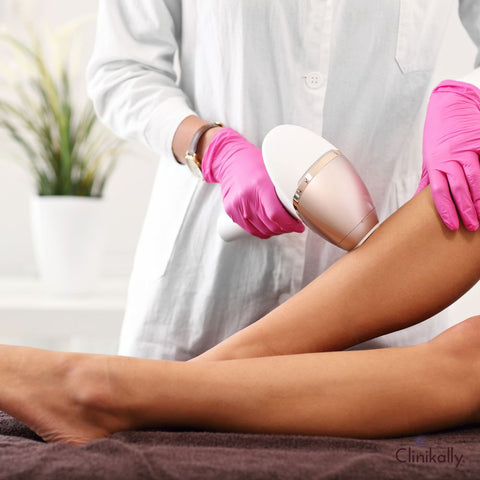
Professional tan removal treatments can effectively eliminate tan lines, uneven pigmentation, and unwanted tans caused by sun exposure, self-tanners, or other factors. The following are some common professional tan removal treatments available at skincare clinics or spas:
-
Chemical peels use exfoliating agents, such as alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), to remove the outer layer of dead skin cells and promote skin regeneration. This can help to fade tan lines, reduce hyperpigmentation, and improve skin tone and texture.
-
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive exfoliation method that employs a handheld device to gently remove the outer layer of dead skin cells. This can help to lighten tan lines, smooth skin texture, and increase collagen production, resulting in a more even complexion.
-
Laser skin resurfacing treatments, such as fractional laser therapy or intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy, focus on pigmented areas of the skin to break up melanin deposits and promote skin renewal. These treatments can effectively reduce tan lines, sunspots, and hyperpigmentation while requiring minimal downtime.
-
Chemical depigmentation treatments, such as laser toning or chemical peels containing depigmenting agents such as hydroquinone or kojic acid, can help to lighten dark patches of skin and even out the tone. These treatments are commonly used to treat persistent hyperpigmentation or melasma.
-
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy unwanted pigmented areas of the skin. This can help remove stubborn tan lines and dark spots, but multiple treatment sessions may be required for best results.
-
Skincare professionals may recommend prescription-strength topical treatments like retinoids, hydroquinone, or corticosteroids to lighten tan lines and improve overall skin tone. These treatments are commonly used in conjunction with professional procedures to achieve better results.
-
Skincare clinics frequently provide medical-grade skincare products containing active ingredients such as retinoids, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), or vitamin C to help lighten tan lines, reduce hyperpigmentation, and promote skin renewal. These products are formulated to deliver potent ingredients for visible results.
Before starting any professional tan removal treatment, you should consult with a qualified dermatologist or skincare professional to determine the best treatment plan for your skin type, concerns, and goals. They can evaluate your skin condition, recommend appropriate treatments, and provide personalised skincare advice to achieve the best results while reducing the risk of complications.
Overview of chemical peels for tan removal
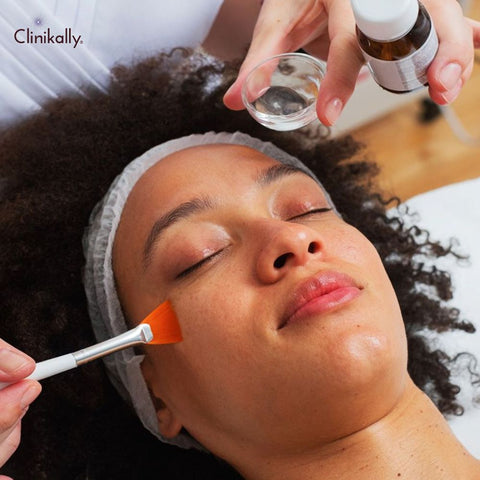

Chemical peels are cosmetic treatments that use various chemical solutions to exfoliate the skin, remove dead skin cells, and stimulate skin renewal. They can help with tan removal by fading tan lines, reducing hyperpigmentation, and improving overall skin tone and texture. This is an overview of chemical peels for removing tans.
-
Types of Chemical Peels: Superficial peels, also known as light peels, exfoliate the skin's outermost layer (epidermis) with mild acids like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs). These peels are ideal for mild tan lines or superficial pigmentation, and they usually require little to no downtime. Medium peels go deeper into the skin and may use stronger acids like glycolic acid or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to target the skin's middle layers (dermis). They work well for moderate tan lines and hyperpigmentation, but recovery may take several days. Deep peels are the most powerful type of chemical peel, penetrating deep into the dermis to treat severe tan lines, pigmentation, and skin imperfections. They frequently use phenol or high concentrations of TCA and necessitate extensive downtime for healing.
-
How They Work: Chemical peels work by applying a chemical solution to the skin, resulting in controlled exfoliation and removal of the outer layer of dead skin cells. This exfoliation procedure promotes cell turnover and collagen production, resulting in smoother, brighter, and more evenly toned skin. The type and concentration of acids used in the peel determine the depth of penetration and exfoliation.
-
Benefits for Tan Removal: Chemical peels can effectively lighten tan lines, sunspots, and hyperpigmentation by stimulating the shedding of pigmented skin cells and the formation of new, evenly pigmented skin. They can also improve overall skin texture, minimise fine lines and wrinkles, and boost skin radiance for a more youthful appearance. Chemical peels are adaptable to the individual's skin type, concerns, and desired outcome, allowing for personalised treatment plans.
-
Treatment Process: Before the peel, the skin is thoroughly cleansed and prepared to remove any oils or debris. The chemical solution is then applied to the skin in a controlled manner, and the treatment area may feel tingly or burned. After a set amount of time, the peel is neutralised or washed away, and a soothing moisturiser or post-peel treatment is applied to the skin. Depending on the depth of the peel and the individual's skin response, multiple treatment sessions may be required for best results.
-
Aftercare and Recovery: After a chemical peel, the skin may appear red, sensitive, and flaky, similar to a sunburn. It's essential to follow post-treatment instructions provided by the skincare professional to support healing and minimize complications. Sun protection is essential during and after the recovery period to protect newly exposed skin from UV damage and prevent the recurrence of tan lines and hyperpigmentation.
Laser therapy options for pigmentation correction
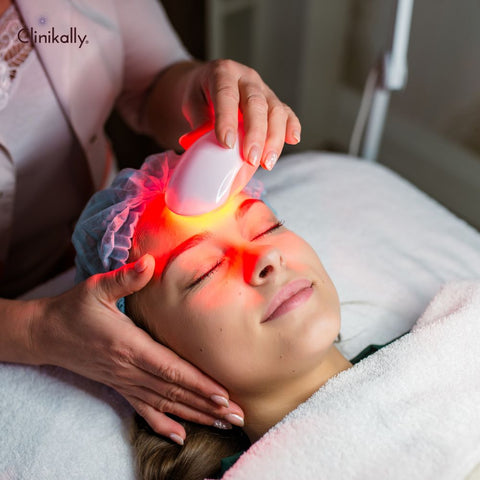
Laser therapy provides several pigmentation correction options, including tan lines, sunspots, freckles, melasma, and other forms of hyperpigmentation. Here's an overview of commonly used laser therapy options for pigmentation correction:
-
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: IPL therapy directs broad-spectrum light energy at pigmented lesions, stimulating the skin's natural healing response. It effectively treats sunspots, age spots, freckles, and uneven pigmentation caused by sun exposure. IPL therapy is non-invasive, has minimal downtime, and can be tailored to the individual's skin type and pigmentation concerns.
-
Fractional Laser Therapy: Fractional laser therapy uses laser energy in tiny, fractionated beams to form microthermal zones in the skin, which promotes collagen production and skin renewal. Fractional lasers can treat specific areas of hyperpigmentation while leaving the surrounding skin unaffected, reducing downtime and side effects. This treatment effectively reduces pigmented lesions, improves skin texture, and rejuvenates the skin as a whole.
-
Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser: Q-Switched Nd:YAG lasers produce high-intensity light pulses in short bursts, which target melanin deposits in the skin without causing damage to surrounding tissues. This laser is especially effective at treating stubborn pigmented lesions like melasma, age spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Multiple treatment sessions may be required for the best results, with minimal downtime and side effects.
-
Picosecond Laser: Picosecond lasers use ultra-short pulses of laser energy to precisely target pigmented cells. Picosecond lasers are extremely effective at treating difficult-to-remove pigmented lesions such as tattoos, birthmarks, and melasma. The rapid pulses of energy reduce heat buildup in the skin, lowering the risk of side effects and downtime.
-
Fractionated Erbium or CO2 Lasers: Fractionated erbium or CO2 lasers deliver precise laser energy to specific areas of the skin, removing superficial layers and stimulating collagen remodelling. These lasers effectively treat sun damage, uneven pigmentation, and textural irregularities, resulting in smoother, more even-toned skin. Fractionated lasers can be tailored to each individual's skin type, concerns, and desired outcome, with varying degrees of aggressiveness and downtime.
-
Combination Therapies: In some cases, a combination of laser therapies, such as IPL with fractional laser or picosecond laser with Q-switched laser, may be recommended to address multiple pigmentation concerns and achieve complete results. Combination therapies can address multiple layers of the skin, providing synergistic benefits for pigmentation correction and skin rejuvenation.
Before undergoing laser therapy for pigmentation correction, you should consult with a board-certified dermatologist or experienced skincare professional to evaluate your skin condition, determine the best treatment approach, and discuss potential risks and benefits. They can create a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs and goals, resulting in safe and effective pigmentation correction with minimal downtime and optimal outcomes.
Microdermabrasion and its effectiveness in tan removal

Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive cosmetic procedure in which a handheld device exfoliates and removes the outer layer of dead skin cells, revealing smoother, brighter, and more evenly toned skin. While microdermabrasion can improve skin texture and reduce mild pigmentation irregularities, its efficacy in removing tans may be limited when compared to other treatments specifically designed to correct pigmentation. Here's an overview of microdermabrasion and its effectiveness in removing tans.
-
During a microdermabrasion treatment, a specialised device uses fine crystals or a diamond-tipped wand to gently exfoliate the skin's surface. Exfoliation removes dead skin cells, unclogs pores, and stimulates the regeneration of healthy skin cells, resulting in a smoother, more radiant complexion. Microdermabrasion promotes collagen production and increases blood circulation, resulting in improved skin texture and tone over time.
-
Microdermabrasion can help lighten tan lines and reduce superficial pigmentation irregularities by exfoliating the skin's outermost layer. By removing dead and damaged skin cells, microdermabrasion may reveal fresher, lighter skin underneath, which can contribute to a more even skin tone. Microdermabrasion is especially effective for removing mild tan lines, sunspots, and surface pigmentation caused by sun exposure, self-tanning, or other factors.
-
While microdermabrasion can help with tan lines and superficial pigmentation, it may not be as effective for deeper pigmentation or stubborn tan lines. Microdermabrasion primarily targets the skin's outermost layer (epidermis), and it may not penetrate deeply enough to reach deeper layers that cause pigmentation irregularities. Deeper pigmentation issues, such as melasma or stubborn tan lines, may necessitate more targeted treatments, such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or topical depigmenting agents, for the best results.
-
Microdermabrasion can be combined with other pigmentation-correcting treatments, such as chemical peels or topical depigmenting agents, to improve outcomes and address a variety of pigmentation irregularities. Combining microdermabrasion with complementary treatments can aid in more comprehensive tan removal and skin rejuvenation, particularly for people with moderate to severe pigmentation issues.
-
To maintain the results of microdermabrasion for tan removal, regular treatments may be recommended, usually spaced several weeks apart. Sun protection measures, such as using sunscreen and seeking shade, are also necessary to avoid future tan lines and protect the skin from UV-induced pigmentation.
Takeaway: Get rid of tan for smooth even skin tone!
Tan removal from the hands and face necessitates a combination of effective strategies that are specific to the individual's skin type, tan intensity, and desired outcome. Here are some final thoughts on effective tan removal strategies for these areas:
-
Regular exfoliation with a gentle scrub or cleanser can help remove dead skin cells and lighten tan lines on the hands and face. Select exfoliation products that contain beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) for a mild yet efficient exfoliation.
-
Use brightening serums or products with ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, or licorice extract to help fade tan lines and even out skin tone on the hands and face. These ingredients can reduce melanin production and promote skin brightness over time.
-
Targeted treatments, such as spot treatments or creams containing hydroquinone, kojic acid, or retinoids, can help with stubborn tan lines and hyperpigmentation on the hands and face. These ingredients can help lighten pigmented areas and stimulate skin renewal.
-
Professional chemical peels, such as glycolic acid or salicylic acid peels, can help remove tan and hyperpigmentation from the hands and face. These treatments exfoliate the skin and stimulate cell turnover, resulting in a brighter, more even complexion.
-
Consider laser therapy options like IPL therapy or fractional laser resurfacing for targeted tan removal and pigmentation correction on the hands and face. These treatments can effectively lighten tan lines, sunspots, and hyperpigmentation while requiring minimal downtime and side effects.
-
Daily use of sunscreen with a high SPF and broad-spectrum protection will protect the hands and face from further sun damage. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially if you spend a lot of time outside, to avoid tan lines and pigmentation.
-
Keep your skin hydrated and moisturised to promote skin health and aid in the natural exfoliation process. To keep the skin hydrated and the barrier functioning, use a hydrating moisturiser with ingredients like hyaluronic acid or ceramides.
-
Consistency and patience are required to effectively remove tans from the hands and face. Incorporate targeted treatments into your skincare routine and follow a consistent sun protection regimen to see gradual improvements over time.
By combining these strategies and creating a skincare regimen tailored to your specific needs, you can effectively remove tan from your hands and face, resulting in a brighter, more even complexion. Remember to consult a dermatologist or skincare professional for tailored recommendations and advice based on your skin type and concerns.















1 comment
Riya Kumari
How to remove tan from face
How to remove tan from face