The crucial step of "sun protection" must not be disregarded when treating and preventing melasma. Sun protection is critical in the treatment of melasma since UV rays from the sun can initiate and aggravate the condition. Here are some of the reasons why sun protection is such an important part of melasma care. UV radiation causes melasma, prevents darkening and recurrence, and improves treatment outcomes and general skin health. Remember that constant and attentive sun protection is essential for controlling melasma and preventing its severity or recurrence. Consult a dermatologist for tailored advice and recommendations tailored to your unique problem and skin type.
The Basics: What Is Melasma?
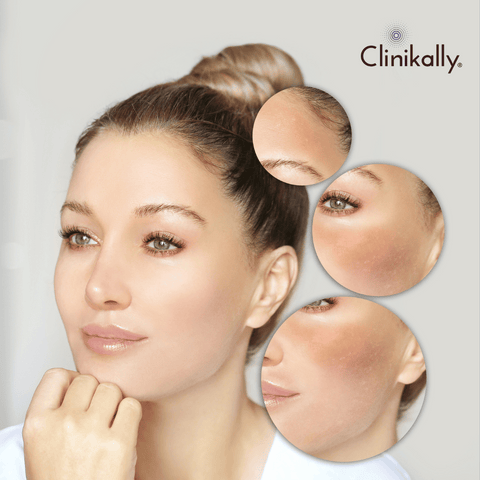

Melasma is a common skin disorder that causes dark or grayish-brown patches to appear on the skin. It is most common on the face, although it can also occur on other sun-exposed regions of the body, such as the neck and arms. Melasma is more common in women, especially those with darker skin tones, but it can affect anyone of any gender or race. Melasma's specific etiology is unknown, however, it is thought to be impacted by a number of variables, including hormone fluctuations, sun exposure, and hereditary predisposition. Hormonal fluctuations, such as those seen during pregnancy or while taking hormonal drugs such as birth control pills, can cause or intensify melasma in people who are predisposed to it. Another essential element is sun exposure, which can stimulate melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) in the skin, resulting in increased melanin production and the creation of melasma patches.
Melasma can show in a variety of ways, but it most often appears as symmetrical patches of discoloration on the face, most commonly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. These patches have definite edges and might be tan, brown, or grayish-brown in color. Melasma is known as the "mask of pregnancy" due to its relationship with hormonal changes during pregnancy. Melasma is a harmless illness that causes no physical discomfort or health issues; nonetheless, it can have a substantial impact on a person's self-esteem and confidence. As a result, many people seek therapy to remove pigmentation and improve the appearance of their skin.
Understanding the Underlying Causes of Melasma
Melasma is a multifaceted illness with numerous underlying causes. While the precise cause is unknown, various factors contribute to the development of melasma. There are several factors that contribute to melasma, but the following are the most significant ones:
-
Melasma is influenced by hormonal changes, as shown by the fact that it affects women more than men when hormones are changing. This includes pregnancy (also known as chloasma or the "mask of pregnancy"), hormonal contraception, hormone replacement therapy, and hormonal imbalances. Melasma patches can develop when estrogen and progesterone levels are high.
-
Sun exposure is a major cause of melasma. Sunlight stimulates the activity of melanocytes, which are responsible for the production of melanin. Melasma is characterized by dark patches that are brought on by an increase in melanin production. Sunlight exposure can exacerbate existing melasma and raise the possibility of developing new patches.
-
There is evidence that suggests genetic predisposition may affect how melasma develops. People with melasma are more likely to develop it themselves because it runs in families. Some people may be more prone to developing melasma due to genetic factors that affect how melanocytes react to hormonal and environmental triggers.
-
Melasma is more prevalent in people of darker skin tones, such as Fitzpatrick skin types III to VI. Melanocytes can aggravate melasma, and they are more common in people with darker skin because they produce more melanin. Furthermore, people with melasma are more likely to be Hispanic, Asian, or Middle Eastern.
-
Other factors that may contribute to the development or worsening of melasma include certain medications (such as antiseizure drugs and some cosmetics), hormonal disorders (such as polycystic ovary syndrome), and certain medical conditions.
Identifying the Different Types of Melasma
Based on the distribution and location of the pigmentation on the skin, melasma can be divided into various types. There are three primary types of melasma:
-
Epidermal Melasma: This type of melasma is characterized by an increase in melanin production in the top layer of the skin (epidermis). It appears as dark brown patches with sharp borders. Epidermal melasma is usually treatable and may improve with topical creams or other interventions that target the skin's outer layer.
-
Dermal Melasma: Dermal melasma is characterized by an increased concentration of melanin in the skin's deeper layer (dermis). The pigmentation appears as bluish-gray or light brown patches with less defined borders than epidermal melasma. Dermal melasma is more difficult to treat because the pigmentation is deeper within the skin.
-
Mixed Melasma: As the name implies, this condition is a combination of epidermal and dermal melasma. It appears as patches with well-defined and less-defined borders and pigmentation of light brown, dark brown, and bluish-gray. Treatment for mixed melasma may necessitate a multifaceted approach that targets both the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin.
It is crucial to remember that melasma-type identification is mostly based on clinical examination and can be difficult at times. A dermatologist or skincare specialist who has treated melasma may accurately determine the type of melasma and tailor a treatment plan to fit. Melasma can also be classified based on where it appears on the face, in addition to the categories indicated above. Examples of typical patterns include:
-
Centrofacial Melasma: This is the most common pattern of distribution and involves pigmentation on the central areas of the face, such as the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and nose.
-
Malar Melasma: Malar melasma is a type of pigmentation that appears on the cheeks as a "butterfly" or "mask-like" appearance.
-
Mandibular Melasma: Melasma that affects the jawline and chin area.
-
Extrafacial Melasma: Melasma can spread beyond the face to other sun-exposed areas such as the neck, chest, and arms in some cases.
Decoding the Melasma Management Regimen: Steps to Success
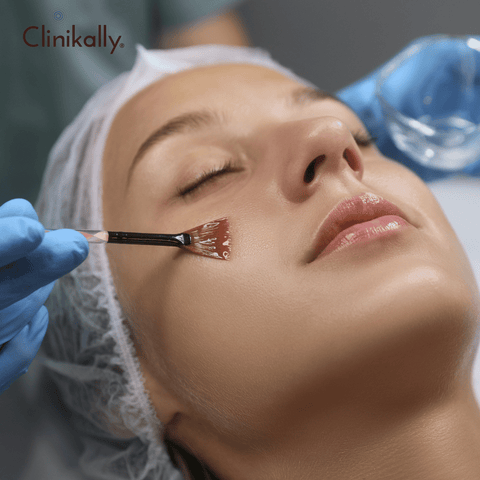
To be successful in managing melasma, a comprehensive approach combining various strategies is required. You can use the pigmentation cream along with, a following are the steps to developing an effective melasma management regimen:
-
Consult a Dermatologist: To begin, see a dermatologist who specializes in the treatment of melasma. They will evaluate your condition, determine the severity of your melasma, and make personalized treatment recommendations.
-
Sun Protection: It is critical to protect your skin from the sun when dealing with melasma. Sun exposure can aggravate melasma and cause increased pigmentation. Use the following sun protection measures:
-
Even on cloudy days, apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to your face, neck, and other exposed areas.
-
Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more often if you are sweating or swimming.
-
To protect your skin from direct sunlight, wear protective clothing such as wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses.
-
Seek shade, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
-
Topical Treatments: Dermatologists frequently prescribe topical medications to treat melasma. Options that are frequently used include:
-
Hydroquinone: This depigmenting agent aids in the removal of dark spots. It can be used on its own or in conjunction with other topical treatments.
-
Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives aids in the reduction of melasma by improving skin texture and promoting cell turnover.
-
Azelaic acid: It aids in the normalization of melanin production and can be used as an alternative to hydroquinone.
-
Kojic acid: This natural ingredient inhibits melanin production and is frequently used in conjunction with other treatments.
-
Combination Therapy: Combining different topical treatments may improve their efficacy in some cases. Your dermatologist may recommend a customized combination of hydroquinone, retinoids, and other topical agents.
-
Chemical Peels: Chemical peels entail the application to the skin of a chemical solution that exfoliates the top layer and stimulates skin renewal. Chemical peels can help lighten melasma and improve skin texture. They are frequently performed in the office of a dermatologist.
-
Laser and light therapies: Melasma can be treated with a variety of laser and light therapies. These treatments work by dissolving excess melanin and stimulating collagen production. Popular alternatives include:
-
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): IPL targets irregular pigmentation and can help lighten melasma.
-
Fractional Laser: This laser treatment resurfaces the skin and has been shown to be effective in the treatment of melasma.
-
Q-switched lasers: These lasers specifically target melanin and can help lighten dark spots.
-
Maintenance and follow-up: Melasma management is an ongoing process. Following improvement, it is critical to follow your dermatologist's recommended maintenance regimen. This usually entails applying sunscreen on a regular basis, using topical treatments, and scheduling follow-up appointments on a regular basis.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Certain lifestyle factors can contribute to melasma. Consider including the following habits in your daily routine:
-
Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that aggravate your melasma, such as excessive sun exposure, hormonal fluctuations, and certain cosmetic products.
-
Gentle skincare: For sensitive skin, use gentle cleansers and skincare products. Harsh cosmetics can irritate the skin and worsen melasma.
-
Stress management: Stress can disrupt hormonal balance and worsen melasma. Exercise, meditation, and hobbies are all stress-relieving activities.
The Importance of Sun Protection in Melasma Care
Sun protection is critical in the treatment of melasma. Here's why it is important in melasma management:
-
Prevents Melasma Triggering and Exacerbation: Sun exposure is a major cause of melasma. The sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation stimulates the production of melanin (pigment), causing existing melasma patches to darken and new ones to form. You can help prevent melasma from worsening and new patches from forming by protecting your skin from the sun.
-
Reduces Pigmentation: The presence of hyperpigmented patches on the skin distinguishes melasma. Sun protection measures, such as wearing sunscreen and protective clothing, aid in the reduction of pigmentation by preventing the activation of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) and the subsequent production of excess melanin. Consistent sun protection can cause existing melasma patches to lighten over time.
-
Enhances Treatment Effectiveness: Melasma is typically treated with a variety of methods, including topical medications, chemical peels, and laser therapies. However, when used in conjunction with sun protection, these treatments are more effective. Sun exposure can negate the effects of treatment and cause melasma to return or worsen. You maximize the effects of your selected treatment plan by consistently using sun protection.
-
Maintains Long-Term Results: Ongoing maintenance and care are necessary for melasma management. Even after melasma has improved, maintaining the effects of sun protection is crucial. Without sufficient sun protection, the melasma patches may darken once more, which could cause the condition to relapse. The long-term effects of your melasma treatment can be maintained by incorporating sun protection into your daily routine.
-
Supports Overall Skin Health: Sun protection is essential for managing melasma as well as preserving the general well-being and aesthetics of your skin. Long-term sun exposure without protection can result in early aging, fine lines, uneven skin tone, wrinkles, and a higher risk of developing skin cancer. You support the health of your skin and preserve a younger, more radiant complexion by protecting it from damaging UV rays.
Follow these sun protection recommendations to effectively protect your skin from the sun and manage melasma:
-
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen to your hands, face, neck, and any other exposed skin using a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 30 or higher.
-
Every two hours, or more often if you are swimming or perspiring, reapply sunscreen.
-
Wear protective clothing to reduce your exposure to the sun, such as long sleeve shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses.
-
Seek shade, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the UV radiation is at its peak.
You can significantly lower the risk of melasma worsening, encourage skin lightening, improve treatment effectiveness, and maintain long-term results by consistently including sun protection in your melasma care regimen.
The Role of Skin Care Products in Melasma Management

Skincare products are essential for managing melasma because they support overall skin health and complement other treatment modalities. The following are the main features of skin care products in the treatment of melasma:
-
Gentle Cleansers: Melasma sufferers must make sure they select a gentle cleanser. Harsh cleansers can damage the skin barrier and strip the skin of its natural oils, causing irritation and possibly exacerbating melasma. Choose gentle, non-abrasive cleansers that remove dirt and debris from the skin thoroughly without endangering or irritating it.
-
Moisturizers: Maintaining healthy skin and supporting the efficacy of melasma treatments both depend on proper hydration. Look for moisturizers that are suitable for your skin type and are non-comedogenic. Skin that is properly hydrated is less prone to inflammation and can handle other topical treatments better.
-
Sunscreen: As was previously mentioned, sun protection is crucial for melasma management. A broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher is recommended. Search for products that offer both UVA and UVB protection. As they offer a physical barrier against UV rays, physical sunscreens with ingredients like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are frequently preferred.
-
Topical Agents for Pigmentation: Melasma patches can be lightened, and pigmentation can be targeted with a number of topical agents. These may consist of hydroquinone, retinoids, azelaic acid, kojic acid and vitamin C.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Substances: Inflammation can lead to the onset and exacerbation of melasma. Melasma can be controlled by applying topical medications with anti-inflammatory properties. You should search for ingredients like niacinamide, licorice extract, green tea extract, and aloe vera.
-
Exfoliating Agents: Exfoliation on a regular basis can help eliminate dead skin cells and increase the absorption of other topical therapies. However, using moderate exfoliating chemicals is critical, since excessive exfoliation can irritate the skin and aggravate melasma. When used correctly, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) such as glycolic acid and lactic acid, as well as beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) such as salicylic acid, can be useful.
-
Antioxidants: Antioxidants can promote overall skin health and protect the skin from oxidative stress. Seek out products that contain antioxidants like niacinamide, vitamin E, green tea extract, or resveratrol. These components might also make the skin appear more radiant.
The Overlooked Step: How Skipping This Can Worsen Melasma
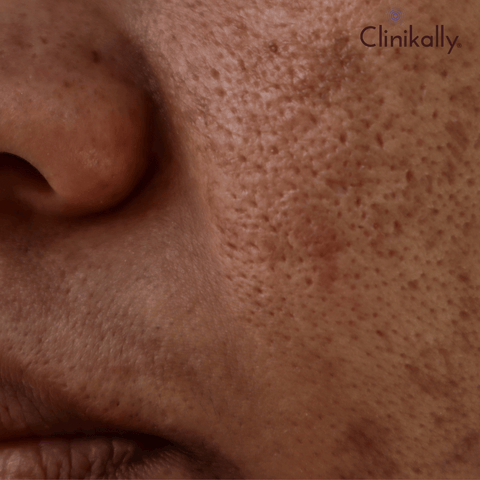
Melasma is a common skin disorder that causes dark or greyish spots to appear on the face, mainly on the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, and upper lip. It is more common in women and is frequently linked to hormone changes, UV exposure, and genetic factors. While there are numerous causes that might aggravate melasma, one usually ignored step that can contribute to its exacerbation is failing to apply sunscreen.
Sunscreen is essential in the treatment of melasma. The sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a key cause of melasma because it stimulates the formation of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. When the skin is not protected from the sun, UV radiation can enhance the pigmentation of existing melasma patches and possibly cause the growth of new ones. This is why melasma patients must apply sunscreen religiously and consistently.
This is why skipping sunscreen can make melasma worse:
-
Increased pigmentation: The cells that produce melanin, called melanocytes, are stimulated to grow as a result of UV radiation. These cells are already overactive in people who are prone to developing melasma. Melasma patches become darker and more pigmented when exposed to UV rays without wearing sunscreen. This stimulation causes further growth of the condition.
-
Deepening of pigmentation: Melasma is known to affect both the dermis and the epidermis, the deeper layers of the skin. UV rays can penetrate the dermal layers of the skin, increasing pigment production and giving the melasma patches a deeper, more pronounced appearance.
-
Delayed fading: Topical medications, chemical peels, and laser therapy are frequently used to treat melasma effectively. However, the advantages of these treatments may be reduced in the absence of adequate sun protection. UV exposure can lengthen the time it takes for melasma patches to fade or disappear, which can counteract the fading effects of these treatments.
It is essential to incorporate sun protection measures into your daily routine to prevent melasma from getting worse. Here are a few advice:
-
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen: Pick a sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) and broad-spectrum protection, which provides protection from UVA and UVB rays. It should be liberally applied to all exposed skin, including the face, neck, and any other melasma-affected areas.
-
Reapply sunscreen frequently: You should reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you are swimming or perspiring a lot. It is crucial to maintain protection throughout the day because even water-resistant sunscreens can deteriorate.
-
Seek shade: To reduce direct sun exposure, try to stay as much in the shade as you can between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the sun is at its heaviest.
-
Wear protective clothing: To further shield yourself from the sun's harmful rays, wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and clothing that covers your skin.
-
Consider using sunscreen all year round: Even on cloudy days and in the winter, UV radiation can still penetrate your skin. Make applying sunscreen a habit year-round, regardless of the climate.
The Critical Role of Sunscreen in Melasma Care
Melasma treatment and management must include the use of sunscreen. Melasma is a complicated disease influenced by a number of factors such as hormonal changes, heredity, and sun exposure. Sunscreen is an important part of a comprehensive treatment plan, but it may not be sufficient on its own to treat melasma. Some of the reasons why sunscreen is essential for melasma treatment are as follows:
-
UV radiation protection: The sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a major cause of melasma. It promotes the synthesis of melanin, which results in the appearance of dark patches on the skin. Sunscreen serves as a barrier to protect the skin from damaging UV rays and lowers the possibility of melasma worsening or developing new patches.
-
Preventing changes in pigmentation: Wearing sunscreen helps stop the emergence of new melasma patches as well as the worsening of already present ones. It prevents UV rays from stimulating the production of melanin, lowering the risk of hyperpigmentation and melasma pigmentation deepening.
-
Enhances the efficacy of other therapies: Topical creams, chemical peels, and laser therapies are all used to treat melasma in order to reduce pigmentation and even out skin tone. However, these treatments might be less effective or their effects might be fleeting without the right sun protection. Sunscreen enhances these procedures by preventing UV rays from negating their fading effects and fostering longer-lasting effects.
-
Treatment outcomes must be maintained: Melasma is a chronic condition that must be managed on an ongoing basis. Melasma can recur or worsen even after successful treatment if it is not properly maintained. Sunscreen use is critical for avoiding relapses and maintaining the results of various treatment modalities.
-
Prevention of sun-related skin damage: In addition to melasma, unprotected sun exposure can cause sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. You can protect your skin from these harmful effects and maintain overall skin health by incorporating sunscreen into your daily routine.
Choosing the Right Sunscreen for Melasma
Choosing the best sunscreen for melasma is an important step in effectively managing the condition. Here are some things to think about when choosing sunscreen:
-
Broad-spectrum protection: Choose a sunscreen that offers broad-spectrum protection, meaning it protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Both types of UV radiation can cause melasma and other skin damage. The words "broad-spectrum" should be present on the sunscreen label.
-
Sun Protection Factor (SPF): Choose a sunscreen with a high SPF, preferably one with an SPF of 30 or greater. SPF denotes the level of protection against UVB rays, which are the primary cause of sunburn. However, bear in mind that SPF does not primarily determine UVA protection, so make sure the sunscreen provides broad-spectrum coverage.
-
Chemical versus physical sunscreen: Physical (mineral) and chemical sunscreens are the two main categories. Physical sunscreens have active components like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide that physically shield the skin from UV rays by reflecting and diffusing them. On the other hand, chemical sunscreens contain chemicals that absorb UV rays and turn them into heat. Physical sunscreens might be less irritating and better tolerated by some melasma sufferers. To find out which is best for your skin, think about attempting both.
-
Non-comedogenic and gentle formula: Look for sunscreens that are non-comedogenic, which means they will not clog pores or cause acne breakouts. Because melasma-prone skin is more sensitive, choose a sunscreen with a gentle formula that is less likely to irritate or inflame it.
-
Fragrance-free: Fragrances can irritate the skin, particularly for those with sensitive skin or melasma. Choose fragrance-free sunscreens to reduce the risk of skin reactions.
-
Water-resistant: If you plan on sweating or swimming, choose a sunscreen that is water-resistant and can provide protection even during these activities. However, keep in mind that water-resistant sunscreens must still be reapplied after a certain amount of time, as specified on the product label.
-
Consider additional features: Some sunscreens include tinted formulas, which can help to even out skin tone and conceal melasma patches. These can be useful if you want some coverage while still protecting your skin.
Dietary Considerations for Melasma: Foods to Include and Avoid

While no single diet may cure melasma, various dietary choices may help maintain general skin health and potentially complement melasma care. Here are some nutritional options to think about:
Include:
-
Antioxidant-rich foods: Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables because they are high in antioxidants. Antioxidants protect the skin from free radicals and oxidative stress, both of which can cause skin damage. Berry, citrus fruits, leafy greens, tomatoes, and bell peppers are examples of antioxidant-rich foods.
-
Vitamin C-rich foods: Vitamin C is necessary for collagen production and skin health. Include foods high in vitamin C, such as oranges, strawberries, kiwis, broccoli, and bell peppers.
-
Foods high in vitamin E: Vitamin E is another antioxidant that may have skin-protective properties. Include vitamin E-rich foods like almonds, sunflower seeds, spinach, and avocados in your diet.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids: Include foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and may benefit overall skin health. Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel, as well as walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, are excellent sources.
-
Colorful vegetables and fruits: Choose a variety of colorful vegetables and fruits because they contain a variety of beneficial compounds such as vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that promote overall health.
Avoid or Limit:
-
Excess sugar consumption: A high sugar and refined carbohydrate intake may contribute to inflammation and harm skin health. Limit your intake of sugary foods, sodas, desserts, and processed snacks.
-
Food triggers: Some people may find that certain foods trigger or worsen their melasma. While triggers vary by individual, common culprits include spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods. If you notice that certain foods aggravate your melasma, try reducing or eliminating them from your diet.
-
Food allergens or sensitivities: If you have known food allergies or sensitivities, it is best to avoid those foods because they can cause inflammation or other reactions that can harm your skin.
Foods that Can Help Prevent and Manage Melasma
While there is no one meal that will prevent or cure melasma, a well-balanced and nutrient-dense diet helps promote general skin health and may help with melasma treatment. Here are some foods that could help:
-
Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are high in antioxidants, which help protect the skin from free radical damage. They are also high in vitamin C, which aids in collagen production.
-
Citrus fruits: Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, and others are high in vitamin C, which is necessary for collagen synthesis and skin health.
-
Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and other leafy greens are high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which promote overall skin health. They are also high in folate, which is necessary for cell regeneration.
-
Tomatoes: Tomatoes are high in lycopene, an antioxidant that may help protect the skin from UV damage. They also have vitamin C and other beneficial ingredients.
-
Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and may benefit skin health. Omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and may be beneficial to melasma patients.
-
Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are high in vitamin E, an antioxidant that helps protect the skin from oxidative stress. They also contain essential fatty acids, which help maintain skin health.
-
Colorful vegetables and fruits: Include a variety of colorful vegetables and fruits in your diet because they contain vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote overall skin health.
-
Green tea: Polyphenols in green tea have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of green tea may help protect the skin from UV radiation damage and promote skin health.
-
Water: Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Drink plenty of water daily to keep your skin hydrated and toxins at bay.
Foods that May Worsen Melasma
While there is no definite list of foods that directly cause or worsen melasma, certain dietary factors may trigger or exacerbate melasma symptoms in certain people. It is crucial to note that these effects might differ from person to person, and what may worsen melasma in one person may not have the same effect on another. Some people have reported the following dietary variables as probable triggers:
-
Foods that are spicy: Foods that are spicy, especially those that contain capsaicin, may widen blood vessels and possibly intensify skin redness and flushing. Some melasma sufferers claim that eating spicy foods makes their condition worse.
-
Caffeine: Although there is little evidence linking caffeine to melasma, some people have claimed that consuming large amounts of caffeinated drinks like coffee, tea, and energy drinks makes their melasma worse. It is well known that caffeine stimulates the release of stress hormones, which may disrupt hormonal balance and result in melasma.
-
Alcohol: Drinking alcohol has been linked to higher estrogen levels, which may cause or aggravate melasma in people who are sensitive to hormonal changes. Additionally, alcohol can widen blood vessels and intensify skin redness.
-
Foods high in histamine: Histamine is a chemical that plays a role in allergic reactions and inflammatory responses. Some melasma sufferers claim that histamine-rich foods, such as aged cheese, cured meats, fermented foods, and particular fish, can make their condition worse.
-
Food sensitivities or allergies: These conditions can aggravate already existing skin conditions by causing inflammation. It may be beneficial to stay away from certain foods if you have known food allergies or sensitivities.
It is important to remember that these speculative causes may not apply to all cases of melasma and are supported only by anecdotal evidence. It is wise to pay close attention to your own particular reactions and keep track of any potential connections between your diet and the symptoms of melasma. If you feel that certain foods are exacerbating your melasma, keep a food diary and talk to a healthcare expert, such as a dermatologist or qualified dietitian, about your concerns and suggested dietary changes. They can provide you with personalized advice based on your individual needs and help you figure out the best way to manage your melasma.
Holistic Approaches to Melasma Management: Beyond Topical Treatments
In addition to topical therapies, there are various holistic ways that can help with melasma care. These methods seek to improve general skin health, treat underlying causes, and promote a healthy lifestyle. Some holistic solutions include sun protection, stress management, hormone balance, diet and nutrition, gut health, natural cures, and expert treatments. Remember that melasma is a complex illness with variable reactions to holistic treatments. It is important to seek the advice of a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or holistic practitioner, who can provide personalized advice based on your individual needs and help tailor a holistic strategy that is right for you.
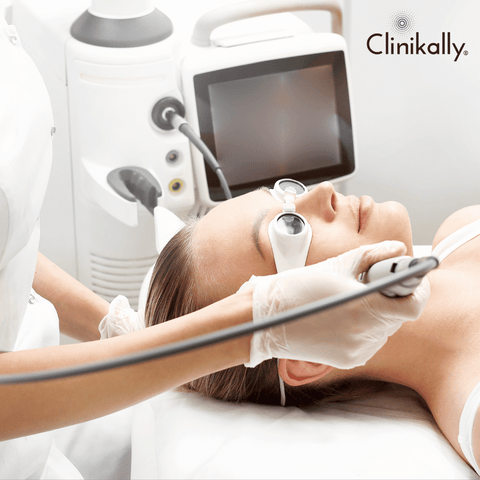
The Benefits of Laser Therapy for Melasma
When alternative therapies have failed to deliver satisfying results, laser therapy might be a viable therapeutic option for melasma. Some advantages of laser therapy for melasma include targeted treatment, precision and control, stimulation of collagen synthesis, gradual lightening of pigmentation, low downtime, conjunction with other treatments, and long-term outcomes. It is critical to speak with a dermatologist or a competent skincare practitioner who specialises in melasma laser therapy. They may evaluate your exact problem, select the best laser therapy choice for you, and develop a personalised treatment plan that suits your specific needs and concerns. To maximise the effectiveness of laser therapy for melasma, it is equally critical to follow post-treatment care recommendations and stick to suggested sun protection practices.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Managing Melasma
Lifestyle modifications can help with melasma management and general skin health. While they do not directly treat melasma, they can help prevent triggers, maintain skin health, and perhaps supplement other treatment options. Sun protection, avoidance of triggers, hormonal balance, stress management, a balanced diet, a skincare routine, and healthy lifestyle habits are some examples of positive lifestyle improvements. Keep in mind that melasma management necessitates a multifaceted strategy, and lifestyle adjustments should be supplemented with various treatment options like topical treatments, professional procedures, or pharmaceuticals. It is best to contact a dermatologist or other healthcare professional who can provide tailored advice and recommendations based on your unique situation and needs.
Key Takeaways: Navigating the Journey to Effective Melasma Management
The process of managing melasma can be difficult, but by taking the following important lessons into account, you can travel the road more successfully:
-
Learn about melasma: Melasma is a skin condition that is frequently seen and is characterized by dark, patchy pigmentation on the face. It is frequently triggered by hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetic predisposition.
-
Seek professional help: Consult a dermatologist or skincare professional who specializes in melasma for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
-
Sun protection is essential: Sun protection is critical in the treatment of melasma. Wear broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, seek shade, and wear protective clothing to reduce sun exposure.
-
Topical therapies: Topical therapies can assist in melasma patch lightening, such as hydroquinone, retinoids, and azelaic acid. Find the best options for your skin by talking to your dermatologist.
-
Laser therapy: Melasma pigmentation can be effectively targeted and lightened with laser treatments. If you want to know if laser therapy is appropriate for your condition, speak with a dermatologist.
-
Holistic approaches: Including lifestyle modifications, such as stress management, balanced nutrition, hormonal balance techniques, and avoiding triggers, can complement other treatment options and enhance general skin health.
-
Patience and consistency: Melasma treatment necessitates both patience and consistency. Results may take time, so it is critical to stick to the treatment plan and follow-up appointments.
-
Ongoing maintenance: Melasma is a chronic condition, and maintenance treatments are frequently required to prevent relapse. Long-term melasma management can be aided by consistent sun protection and adherence to a skincare routine.
-
Psychological support: Melasma can have a negative impact on self-esteem and emotional well-being. Seek help from friends, family, or a mental health professional to address any psychological issues.
Remember that each person's experience with melasma is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is critical to find an approach that meets your specific needs and to seek professional advice throughout the process. Melasma can be effectively managed with time, patience, and the right strategies.









































