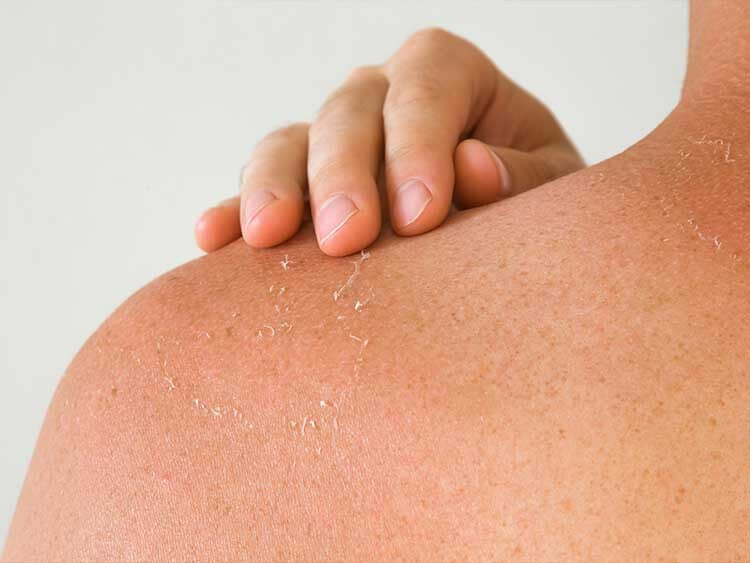
Certainly! A sunscreen is an essential tool for shielding our skin from UV rays and lowering the risk of skin damage and skin cancer. However, there are various misconceptions and fallacies about the use of sunscreen. Remember that appropriate sunscreen application and reapplication are critical for maximum protection. Apply liberally to all exposed skin, including usually ignored regions such as the ears, back of the neck, and tops of the feet. You may enjoy outdoor activities while lowering your risk of skin damage and skin cancer with proper sun protection.
Understanding Sunscreen Basics
Understanding the fundamentals of sunscreen is essential for making educated decisions about protecting your skin from the sun's damaging UV radiation. Sunscreen chemicals, spf (sun protection factor), broad-spectrum protection, water resistance, application and reapplication, sunscreen and expiration dates, and sun protection in all weather conditions are important considerations. Remember that sunscreen is only one component of sun protection. Wearing protective clothes, seeking shelter during peak sun hours, and using sunglasses are all important precautions to take to protect your skin from the sun's harmful rays.
How Sunscreen Works: Protecting Against Harmful UV Rays
Sunscreen works by forming a protective barrier on the skin's surface, preventing or reducing the penetration of harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun. UVA and UVB rays are the two types of UV rays that sunscreen protects against. Before heading outside, apply sunscreen liberally and evenly to all exposed skin, and reapply at least every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating. In addition to other sun protection measures such as seeking shade and wearing protective clothes, using sunscreen effectively can dramatically minimize the risk of sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer caused by UV exposure.
SPF Demystified: What Sun Protection Factor Really Means
The term "SPF" stands for Sun Protection Factor and is a numerical indicator of how well a sunscreen shields the skin from the sun's damaging ultraviolet B (UVB) rays. The SPF value is an important consideration when selecting the best sunscreen for your skin type and intended sun exposure. Here's what the SPF actually means:
-
UVB Ray Protection: SPF specifically measures a sunscreen's effectiveness in shielding the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. It does not directly measure UVA ray protection, which can cause skin aging and contribute to skin cancer. Look for "broad-spectrum" sunscreens that protect against both UVA and UVB rays to ensure broad-spectrum protection.
-
Calculating SPF Effectiveness: The SPF value is a multiplier that indicates how much longer you can stay in the sun without getting sunburned in comparison to how long it would take if you did not use sunscreen.
-
Protection and SPF Values: SPF values typically range from 15 to 100, but higher SPF values do not always imply proportionally better protection. The difference in protection between SPF 30 and SPF 50, for example, is not significant. SPF 30 filters approximately 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 filters approximately 98%. No sunscreen can completely block UV rays.
-
SPF and Skin Type: Different skin types are more or less sensitive to the sun. People with fair or light skin that burns easily are more vulnerable to sunburn and may benefit from sunscreen with a higher SPF. Those with darker skin may prefer a lower SPF, but protection is essential for all skin types.
-
Reapplication Is Key: Regardless of the SPF value, sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours or more frequently if swimming, sweating, or rubbing the skin. Because sweat and water can reduce the effectiveness of sunscreen, reapplying it ensures continued protection.
-
SPF and Sunscreen Effectiveness: While SPF provides valuable protection, it is important to remember that no sunscreen provides complete UV ray protection. Sunscreen should be used in conjunction with a comprehensive sun protection strategy that includes seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and wearing sunglasses.
UVA vs. UVB: The Importance of Broad-Spectrum Protection
Understanding the distinction between UVA and UVB rays, as well as the significance of broad-spectrum protection, is critical for effective sun protection. Both types of ultraviolet rays can cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer, but their characteristics and effects differ:
-
UVA Rays:
-
UVA rays have longer wavelengths and can penetrate deeper into the skin, reaching the dermis—the thickest layer of the skin.
-
These rays are to blame for premature skin aging, such as wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots.
-
UVA rays have also been linked to long-term skin damage and the development of skin cancer, including melanoma, the most dangerous type of skin cancer.
-
UVA rays, unlike UVB rays, are relatively consistent throughout the day and can penetrate clouds and glass, making them a constant threat to the skin even on cloudy or overcast days and indoors.
-
UVB Rays:
-
UVB rays have shorter wavelengths and primarily affect the epidermis, the skin's outermost layer.
-
These rays are responsible for sunburn, which is an immediate reaction to UVB radiation exposure.
-
UVB rays play a significant role in the development of skin cancer, including the two most common types of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
-
The intensity of UVB radiation varies throughout the day, with the highest levels typically occurring at midday when the sun is at its highest point.
Broad-Spectrum Protection is Important: Broad-spectrum sunscreens are designed to protect against both UVA and UVB rays, providing comprehensive coverage against the sun's harmful effects. Here's why broad-spectrum protection is so important:
-
Comprehensive Defense: Broad-spectrum sunscreens shield the skin from a wide range of UV rays, reducing the risk of sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer caused by both UVA and UVB radiation.
-
Preventing Skin Damage: UVA rays can harm the skin permanently, speeding up the aging process and raising the risk of skin cancer. Broad-spectrum sunscreens aid in avoiding these negative consequences.
-
Day-Long Protection: UVA rays are present all day and can pass through glass and clouds. Broad-spectrum sunscreens offer all-day protection, regardless of the weather or indoor/outdoor activities.
Debunking Common Sunscreen Myths

Absolutely! A sunscreen is an important tool for protecting your skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation, but there are several common myths and misconceptions that must be dispelled:
-
Myth: I do not need sunscreen on cloudy days or when I am inside. Fact: UV rays can pass through clouds and windows, so you can be exposed to harmful UV radiation even on cloudy days or when indoors near windows. It's essential to wear sunscreen daily, regardless of the weather or your location.
-
Myth: Using sunscreen is only advised during the summer or at the beach. Fact: UV rays are always present and can harm your skin, even in the winter or on chilly days. Wearing sunscreen is essential for protecting your skin, whether you are at the beach or going about your daily activities.
-
Myth: I can stay in the sun without having to reapply if the SPF is higher. Fact: While higher SPF sunscreens provide more UVB ray protection, no sunscreen is 100% effective. Regardless of the SPF value, you must reapply sunscreen every two hours or after swimming/sweating.
-
Myth: Sunscreen chemicals are hazardous and should be avoided. Fact: When used as directed, sunscreen ingredients approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA, Health Canada, and the European Commission are safe. Studies have shown that the benefits of using sunscreen far outweigh any potential risks.
-
Myth: Sunscreen inhibits your body's ability to produce vitamin D. Fact: While sunscreen can reduce vitamin D production in the skin, it does not completely prevent it. Most people can still get enough vitamin D by eating a healthy diet and getting some sun on their skin that is not covered by sunscreen.
-
Myth: Waterproof or water-resistant sunscreen does not require reapplication after swimming. Fact: No sunscreen is completely waterproof, and even water-resistant sunscreens can lose effectiveness after swimming or sweating. Always reapply sunscreen as directed on the label, especially after swimming.
-
Myth: Sunscreen is only for people with light skin. Fact: Sunscreen can be beneficial for people of all skin types and tones. Everyone can get a sunburn, though those with fair skin may be more at risk. UV radiation is harmful to all living things.
-
Myth: Since sunscreen does not expire, I can use it from last year. Fact: Sunscreen has an expiration date, which is usually indicated on the packaging. Because expired sunscreen may lose its effectiveness, it is critical to check the expiration date and replace any expired products.
Myth #1: You Don't Need Sunscreen on Cloudy Days
Fact: This is a common misconception, but it is incorrect. Clouds do not completely shield the sun's UV radiation. Because UV rays can pass through cloud cover and reach the Earth's surface, you can still get sunburned and suffer skin damage on cloudy days. While the intensity of UV radiation is slightly lower on cloudy days compared to clear, sunny days, the difference is not significant enough to forego sunscreen. UVA rays, which contribute to skin aging, are present throughout the day and can even penetrate windows, so indoor UV radiation exposure is possible.
Myth #2: Higher SPF Offers Unlimited Protection
Fact: While a higher Sun Protection Factor (SPF) provides more UVB protection, it does not provide unlimited protection. The SPF value is a multiplier of the time it takes your skin to burn with sunscreen versus the time without sunscreen. If you normally burn after 10 minutes of sun exposure without sunscreen, an SPF 30 sunscreen would extend that time to 300 minutes (10 minutes x SPF 30 = 300 minutes).
Myth #3: Waterproof Sunscreens Provide All-Day Protection
Fact: While waterproof or water-resistant sunscreens are designed to maintain their effectiveness during water exposure, they do not provide all-day protection. There are some restrictions on how long sunscreen can stay effective while swimming or perspiring, and none of them are completely waterproof.
Maximizing Sunscreen Effectiveness

Follow these recommendations to increase sunscreen effectiveness and guarantee adequate protection from UV rays:
-
Choose the Right Sunscreen: Select a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Look for one that provides protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
-
Apply Generously and Evenly: Use enough sunscreen to cover all exposed skin thoroughly. For most adults, this typically means applying about one ounce (a shot glass full) of sunscreen. Don't forget commonly overlooked areas like the ears, back of the neck, and tops of feet.
-
Apply 15 Minutes Before Sun Exposure: Apply sunscreen at least 15 minutes before going outside to allow the product to bind to the skin and provide optimal protection.
-
Reapply Regularly: Reapply sunscreen every two hours or more frequently if swimming, sweating, or towel-drying. Even water-resistant sunscreens can wear off, so be diligent about reapplication.
-
Use Sunscreen Every Day: UV rays can reach your skin even on cloudy or overcast days. Make wearing sunscreen a daily habit, regardless of the weather.
-
Protective Clothing and Accessories: Wear protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirts, and sunglasses, to shield your skin and eyes from the sun's rays.
-
Seek Shade During Peak Hours: Limit your time in direct sunlight, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when UV rays are most intense.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated and help prevent heat-related issues.
-
Check Sunscreen Expiration Dates: Check the sunscreen's expiration date, and replace any products that have expired to ensure efficacy.
-
Be Mindful of Medications and Skincare Products: Some medications and skincare products can increase your skin's sensitivity to the sun. Check labels and consult with a skin specialists healthcare professional if you're unsure.
-
Protect Children: Use sunscreen specifically formulated for children and keep them in the shade as much as possible. Avoid direct sun exposure for infants younger than six months; dress them in lightweight clothing that covers their skin, and use hats and sunglasses.
Tips for Proper Sunscreen Application
Effective sun protection requires proper sunscreen application. Follow these guidelines to ensure proper sunscreen application and maximize its effectiveness:
-
Use Adequate Amount: Apply enough sunscreen to cover all exposed areas of your skin. Most adults require approximately one ounce (a shot glass full) of sunscreen to cover their entire body.
-
Apply Sunscreen at least 15 minutes before going outside: Apply sunscreen at least 15 minutes before going outside. This allows the sunscreen to adhere to the skin and provide effective protection.
-
Select a Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Look for a sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Choose an SPF of 30 or higher.
-
Cover All Exposed Skin: Do not forget to apply sunscreen to all exposed areas, including your face, neck, ears, arms, legs, and feet. Apply sunscreen to areas that are frequently forgotten, such as the back of the neck and the tops of the feet.
-
Do not Forget Your Lips and Scalp: Use an SPF lip balm to protect your lips from the sun. If you have thinning hair or a bald head, apply sunscreen to your scalp or wear a hat for protection.
-
Reapply Every Two Hours: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you're swimming, sweating, or towel-drying. Even water-resistant sunscreens can wear off.
-
Reapply After Swimming or Sweating: Water can wash off sunscreen, so it's essential to reapply after swimming or heavy sweating.
-
Use Sunscreen Even on Cloudy Days: UV rays can penetrate clouds, so wear sunscreen daily, regardless of the weather.
-
Use Sunscreen Indoors Near Windows: UVA rays can pass through the glass, so if you're indoors near windows, consider applying sunscreen to exposed areas.
-
Avoid Sun Exposure During Peak Hours: Seek shade or stay indoors during peak sun hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV rays are most intense.
-
Check Sunscreen Expiration Date: Check the sunscreen's expiration date, and replace any products that have expired to ensure efficacy.
-
Consider Specific Sunscreen Products: If you have sensitive skin or skin conditions, consider using sunscreens formulated for sensitive skin or physical/mineral sunscreens with ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
Sunscreen and Aging: Preserving Youthful Skin
Sunscreen is critical for preserving youthful skin and slowing the ageing process caused by UV rays from the sun. Here are some tips for keeping your skin looking young:
-
Prevents Premature Aging: UV radiation, particularly UVA rays, is a primary cause of premature aging. They have the ability to degrade collagen and elastin fibres in the skin, resulting in wrinkles, fine lines, and drooping skin. Regular use of sunscreen protects your skin from these damaging consequences and keeps it looking young for longer.
-
Reduces Sunspots and Age Spots: Sunspots and age spots, also known as solar lentigines, are dark areas of skin that form as a result of extended sun exposure. Sunscreens, particularly those with UVA protection, can help prevent the growth and appearance of these spots.
-
Maintains Skin's Elasticity: Sunscreen helps to retain the skin's suppleness and firmness by protecting against collagen and elastin breakdown. As a result, the skin appears smoother and more supple.
-
Prevents Skin Cancer: Sunscreen not only helps with cosmetic concerns, but it also lowers the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma, one of the deadliest forms of cancer. UV ray protection for your skin can have a significant impact on your overall health and well-being.
-
Maintains Even Skin Tone: Sunscreen prevents hyperpigmentation, such as melasma, from developing and helps to even out the skin tone, both of which can be exacerbated by exposure to the sun.
-
Reduces Redness and Inflammation: Sunscreen can help prevent sunburn, redness, and inflammation caused by UVB rays, resulting in healthier and less irritated skin.
To effectively preserve youthful skin and reap the benefits of sunscreen, follow these steps:
-
Choose a sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of 30 or higher.
-
Apply sunscreen liberally and evenly to all exposed skin areas.
-
Wear sunscreen every day, no matter what the weather or season.
-
Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or sooner if swimming, sweating, or towel-drying.
-
Combine sunscreen use with other sun protection measures such as seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and wearing sunglasses.
Sunscreen and Skin Cancer Prevention
Sunscreen is essential for avoiding skin cancer, which is one of the most common and avoidable cancers. Sunscreen can help reduce the risk of skin cancer by preventing sunburns, minimizing cumulative UV damage, protecting against UV rays, reducing the growth of precancerous lesions, and increasing early detection. It is crucial to incorporate sunscreen into your daily routine, as well as regular skin checks and dermatologist visits for any suspected skin abnormalities. By exercising sun-safe practices and protecting your skin from harmful UV radiation, you can significantly reduce your risk of skin cancer and improve your overall skin health.
Choosing the Right Sunscreen for Your Needs

Choosing the best sunscreen for your needs is critical for efficient sun protection and skin health. Broad-spectrum protection, sun protection factor (SPF), skin type and sensitivity, water resistance, formulation and application preferences, ingredients and allergies, fragrance-free option, expiration date, travel-friendly, and brand reputation are all factors to consider when choosing a sunscreen. Remember to apply sunscreen liberally and evenly to all exposed skin regions. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or sooner if swimming, sweating, or towel-drying. Consider other sun protection methods such as seeking shade, wearing protective clothes, and wearing sunglasses to supplement your sunscreen application and properly protect your skin from damaging UV radiation.
Understanding Chemical and Mineral Sunscreens
Chemical and mineral sunscreens are the two main types of sunscreens that provide UV protection from the sun. They work in different ways to protect the skin from UV radiation. The following is a breakdown of each type:
-
Chemical Sunscreens:
-
Organic (carbon-based) compounds in chemical sunscreens absorb UV radiation when applied to the skin.
-
These compounds absorb UV rays and convert them to heat, which is then released from the skin.
-
Chemical sunscreens typically provide UVA and UVB ray protection while remaining lightweight and cosmetically appealing on the skin.
-
Avobenzone, oxybenzone, octinoxate, octisalate, and homosalate are some common chemical sunscreen ingredients.
Advantages of Chemical Sunscreens:
-
In general, it is easier to apply and blend into the skin, with no white cast.
-
Provide broad-spectrum UVA and UVB protection.
-
It may feel more comfortable and lightweight on the skin.
Disadvantages of Chemical Sunscreens:
-
Certain chemical sunscreen ingredients may cause sensitivity or allergic reactions in some people.
-
Chemical sunscreens take 15 to 30 minutes to become fully effective after application because they need time to absorb into the skin.
-
Chemical sunscreens' absorption of UV rays can result in the release of a small amount of heat, which may be uncomfortable for some people with heat-sensitive skin conditions.
-
Mineral Sunscreens (Physical Sunscreens):
-
Mineral sunscreens use inorganic compounds as active ingredients, such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, to form a physical barrier on the skin's surface.
-
When these ingredients are applied to the skin, they reflect and scatter UV rays away from the skin.
-
Mineral sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays and are frequently recommended for people with sensitive skin.
Advantages of Mineral Sunscreens:
-
They are ideal for sensitive skin because they are less likely to irritate or cause allergies.
-
There is no waiting time for them to become effective; they provide immediate protection upon application.
-
When compared to some chemical sunscreens, they are more stable in sunlight and less likely to degrade over time.
Disadvantages of Mineral Sunscreens:
-
Some mineral sunscreens may leave a white cast on the skin, making them incompatible with all skin tones. However, newer formulations have mitigated this problem.
-
They may feel thicker and heavier on the skin than some chemical sunscreens.
Both types of sunscreens have advantages, and the choice between chemical and mineral sunscreens is influenced by personal preferences, skin type, and any specific skin concerns or sensitivities. Finally, the most important aspect is to use sunscreen correctly and on a regular basis, as it protects the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation and reduces the risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
Sunscreen for Sensitive Skin: Gentle Protection
Sunscreen for sensitive skin must be chosen carefully in order to give gentle protection without causing irritation or allergic reactions. When applying some sunscreen chemicals, people with sensitive skin may experience greater redness, irritation, or rashes. Look for mineral sunscreens, avoid fragrances and harsh chemicals, check for hypoallergenic labels, patch test new products, test different formulations, choose broad-spectrum protection, check expiration dates, apply properly, reapply regularly, seek shade, and wear protective clothing. If you have a history of extreme sensitivity or allergic reactions to sunscreen chemicals, see a dermatologist for personalized recommendations and patch testing of specific sunscreen products. Sunscreen is necessary for everyone, including those with sensitive skin, to protect against UV damage and lower the risk of sunburn and skin cancer. Individuals with sensitive skin can enjoy the benefits of sunscreen without irritation with careful selection and proper application.
Sunscreen for Acne-Prone Skin: Clear and Protected
Choosing the right sunscreen for acne-prone skin requires extra care to avoid clogging pores and aggravating existing acne. Here are some pointers for choosing and applying sunscreen to keep your skin clear and protected:
-
Non-Comedogenic Sunscreens: Look for sunscreens that are labeled "non-comedogenic," which means they are less likely to clog pores and cause breakouts. These products are intended to be gentle on acne-prone skin.
-
Choose Oil-Free Formulations: Look for oil-free sunscreens to avoid adding extra oil to your skin and potentially exacerbating acne.
-
Use Gel-Based or Lightweight Lotions: Because gel-based or lightweight lotions have a lighter texture, they are ideal for acne-prone skin. They are less likely to feel greasy on the skin and are absorbed quickly.
-
Avoid Heavy Creams: Heavy creams and thick formulations are more likely to clog pores and should be avoided if you have acne-prone skin.
-
Consider Fragrance-Free Options: Because fragrances can irritate acne-prone skin, look for fragrance-free or unscented sunscreens.
-
Consider Matte Finish: Matte-finish sunscreens can help control excess shine and oiliness on the skin.
-
Antioxidants: Some sunscreens contain antioxidants such as vitamin C or E, which can provide additional benefits for acne-prone skin by neutralizing free radicals and reducing inflammation.
-
Patch Test New Products: Before applying a new sunscreen to your entire face, test it on a small area of the skin to ensure that it does not cause irritation or breakouts.
-
Apply Properly: Apply the sunscreen generously and evenly to all exposed areas of your skin at least 15 minutes before sun exposure.
-
Reapply Regularly: Reapply sunscreen every two hours or more frequently if swimming, sweating, or towel-drying.
-
Avoid Touching Your Face: To reduce the risk of transferring oil and bacteria to your skin, avoid touching your face throughout the day.
-
Cleanse Thoroughly: At the end of the day, thoroughly cleanse your skin to remove sunscreen as well as any accumulated dirt and oil. Use a non-comedogenic cleanser designed for acne-prone skin.
Additional Sunscreen Tips and Considerations

Sunscreen for lips, combination products, sunscreen for scalp and hairline, protective clothing, sunscreen for children, sunscreen for active individuals, sunscreen and medications, be mindful of reflection, sunscreen storage, sunscreen all year round, practice safe tanning and sunscreen for tattoos are some additional sunscreen tips and considerations to help you make the most of your sun protection routine. Keep in mind that sunscreen is only one component of a comprehensive sun protection approach. To reduce UV exposure and protect your skin from the sun's harmful effects, seek shade, wear protective clothes, and use sunglasses in conjunction with sunscreen. Making sun protection a priority will help you preserve the health of your skin and lower your chances of sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer.