Flaky skin is a common condition characterized by dry, rough, scaly, and sometimes itchy patches of skin. Skin becomes dry when it loses water too quickly. This can happen for a variety of reasons. Using deodorant soaps and harsh cleaning products, for example, can strip oils and fats from our skin. Long, hot showers can also dry out your skin. Living in a cold, dry environment dries out the skin as well. In this blog, we will explore more about the common causes of flaky skin, types of flaky skin and available treatments for flaky skin.
Common Causes of Flaky Skin
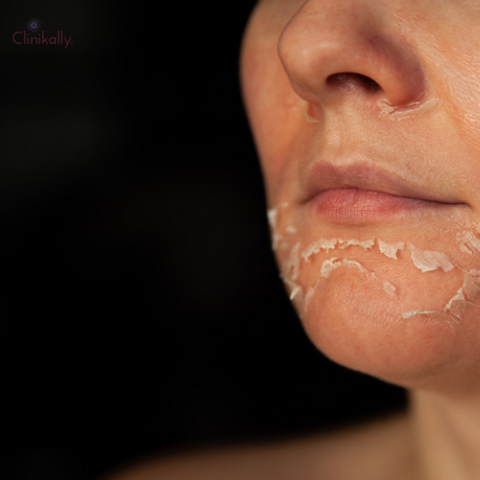

Numerous factors, including the environment and some medical conditions, can contribute to flaky skin. The common causes of flaky skin include:
-
Dry skin: Dry skin is a common cause of flaky skin. It happens when the skin loses too much moisture, and cold weather, low humidity, hot showers or baths, and abrasive soaps or detergents can make it worse.
-
Eczema: Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It can result in flaky skin patches that may be scaly, red, or brown.
-
Psoriasis: Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that speeds up the growth of skin cells. This leads to the buildup of dead skin cells, which can cause flaky skin patches that are thick and silvery-white in color.
-
Seborrheic dermatitis: Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that causes red, itchy, and flaky skin, particularly on the scalp, face, and ears. It is often characterized by dandruff and can be triggered by stress, oily skin, or cold, dry weather.
-
Allergic reactions: Allergic reactions to certain substances, such as fragrances, detergents, or soaps, can cause the skin to become dry, itchy, and flaky.
-
Fungal infections: Fungal infections, such as ringworm or athlete's foot, can cause flaky skin.
-
Medications: Certain medications, such as those used to treat acne or psoriasis, can cause the skin to become dry and flaky.
-
Age: As we grow older, our skin loses moisture and elasticity, resulting in dry, flaky skin.
-
Sun damage: Excessive sun exposure can dry out the skin and damage it, resulting in flaky skin.
It's critical to determine the underlying cause of flaky skin and seek the appropriate treatment. Based on the origin and severity of your flaky skin, your healthcare provider can help you choose the best course of action. Additionally, healthy skincare practices and staying away from irritants like harsh soaps can help prevent flaky skin.
Dry Skin
When the skin loses too much moisture, it can develop dry skin, also referred to as xerosis. It can affect anyone, but those with a history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are more likely to experience it. There are numerous factors that can contribute to dry skin, including:
-
Cold, dry weather: During the winter months, the air is often dry, which can cause the skin to become dry and flaky.
-
Hot showers or baths: Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness.
-
Harsh soaps or detergents: Soaps and detergents that are too strong or contain harsh chemicals can irritate the skin and cause dryness.
-
Aging: As we age, our skin becomes less able to retain moisture, leading to dryness.
-
Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism and diabetes, can cause dry skin.
Symptoms of dry skin may include itching, cracking, and flaking. To prevent and manage dry skin, it is important to take good care of your skin. This includes using a mild, fragrance-free soap and moisturizer, taking short, lukewarm showers or baths, humidifier to add moisture to the air, drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated and avoiding harsh chemicals and irritants.
If you have extremely dry skin or if it's accompanied by other symptoms like redness or swelling, it's imperative that you visit a doctor. They can recommend the best course of treatment to help you manage your symptoms and improve the condition of your skin, such as creams or ointments with prescription-strength ingredients.
Dandruff
Dandruff is a common condition that causes flaking of the skin on the scalp. It is not contagious or dangerous. However, it can be humiliating and difficult to treat. Malassezia is frequently to blame, a yeast-like fungus that can irritate the scalp and hasten skin shedding. Other factors that can contribute to dandruff include:
-
Oily skin: People who have oily skin are more likely to get dandruff because Malassezia can thrive in an environment where there is an abundance of oil.
-
Dry skin: Although less common, dandruff can also occur in people with very dry skin.
-
Not washing your hair enough: If you don't wash your hair often enough, dead skin cells and can lead oily scalp, leading to dandruff.
-
Sensitivity to hair care products: Some people may develop dandruff as a reaction to certain hair care products, such as shampoos or hair sprays.
Skin flakes on the scalp or in the hair, itching, and redness are some signs of dandruff. Over-the-counter dandruff shampoos with active ingredients like zinc pyrithione, salicylic acid, or selenium sulfide are frequently effective at treating mild cases of dandruff. It is crucial to see a healthcare provider if your symptoms are severe or do not improve after trying over-the-counter remedies. They might advise prescription-strength shampoos or medications to help you manage your symptoms and improve the condition of your scalp.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common inflammatory skin condition that mostly affects the scalp, face, and chest because of its high concentration of oil glands. It is characterized by red, itchy, and flaky skin, and is frequently confused with eczema or psoriasis. The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not known, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. The symptoms can also be brought on by or made worse by specific medical conditions, medications, and stress.
Medicated shampoos, creams, and ointments containing antifungal or anti-inflammatory ingredients may be used as a treatment for seborrheic dermatitis. Oral medicines may also be prescribed in some circumstances. In addition, avoiding triggers and maintaining good hygiene, such as regularly washing the affected areas and moisturizing the skin, can help manage the condition.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches to appear on various parts of the body. The condition may cause itchiness, pain, and discomfort and can range in severity from mild to severe. Psoriasis is thought to be brought on by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, though its exact cause is still unknown. The onset of the condition is accompanied by the development of a symbiotic relationship between the symbiotic organism and the host.
Treatment for psoriasis typically involves topical medications, such as creams and ointments, that help to reduce inflammation and slow down the production of skin cells. In more severe cases, oral medications and biological therapies may be prescribed. Additionally, lifestyle modifications like stress reduction and abstaining from triggers like alcohol and smoking may help manage the condition.
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that can be managed but not cured. It might be necessary to receive ongoing care and attention in order to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. To create a successful treatment plan, it is crucial for people with psoriasis to consult with their doctor frequently.
Eczema
Eczema, also referred to as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that results in red, itchy, and inflamed skin. It can occur on any part of the body but is most commonly found on the face, neck, hands, and legs. The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Dry skin, irritants, allergens, stress, and particular foods can all act as triggers to worsen the condition or cause flare-ups.
Most eczema treatments focus on symptom management and outbreak avoidance. This may include avoiding triggers, using gentle skincare products, and applying moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated. In addition, topical medications such as corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and other anti-inflammatory creams may be prescribed to help reduce itching and inflammation. In more severe cases, phototherapy (light therapy) or systemic medications such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologic drugs may be prescribed.
Eczema is a chronic condition that may require ongoing treatment and management. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan and make lifestyle changes to help manage the condition.
Allergies
Allergies are a common condition that occurs when the immune system overreacts to a normally harmless substance, such as pollen, dust, pet dander, or certain foods. The immune system produces antibodies that trigger the release of chemicals, such as histamine, which cause symptoms such as sneezing, itching, runny nose, and rashes. Allergies can be classified into different types based on the type of immune response involved. The most common types of allergies include:
-
Respiratory allergies: These allergies affect the nose, lungs, and airways, and can cause symptoms such as sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, wheezing, and coughing.
-
Skin allergies: These allergies affect the skin and can cause symptoms such as itching, redness, and hives.
-
Food allergies: These allergies occur when the immune system reacts to certain foods and can cause symptoms such as swelling, itching, and digestive problems.
-
Drug allergies: These allergies occur when the immune system reacts to certain medications and can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.
Treatment for allergies may include avoiding triggers, taking medications such as antihistamines, decongestants, and corticosteroids to reduce symptoms, and in some cases, undergoing immunotherapy to desensitize the immune system to the allergen. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan for allergies and to manage symptoms to improve quality of life.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes refer to the natural fluctuations in hormone levels that occur in the body throughout life. Hormones are chemical messengers made by glands in the body that control a variety of vital processes, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Some of the most common hormonal changes that occur in the body include:
-
Puberty: During puberty, the body experiences an increase in sex hormones, including estrogen and testosterone, which causes physical changes such as the development of breasts, pubic hair, and facial hair.
-
Menstrual cycle: The menstrual cycle is a monthly hormonal process that prepares the uterus for pregnancy. It involves the fluctuation of estrogen and progesterone levels in the body, which can cause physical and emotional changes.
-
Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the body undergoes significant hormonal changes to support the growth and development of the fetus. These changes can cause physical changes such as weight gain and mood swings.
-
Menopause: Menopause is a natural hormonal transition that occurs in women usually around the age of 50, where the ovaries stop producing eggs and there's a decrease in the production of estrogen and progesterone in the body. This can cause physical changes such as hot flashes, mood swings, and vaginal dryness.
Hormonal changes can have a significant impact on the body and may cause a variety of physical and emotional symptoms. It is important to understand these changes and work closely with a healthcare provider to manage any symptoms and maintain overall health and well-being.
Climate
Climate is the collective term for the long-term trends in temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind, and other atmospheric conditions that prevail in a given area over time. The climate is influenced by a variety of factors, including latitude, altitude, proximity to large bodies of water, and prevailing winds. These changes are largely attributed to human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and other land-use changes, which have led to an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, trapping more heat and leading to a rise in global temperatures.
Climate change is having significant impacts on the environment, including melting glaciers and sea ice, rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, and changes in ecosystems and wildlife behavior. These changes are also having impacts on human health, including increasing the incidence of heat-related illnesses and respiratory problems. Mitigating and adapting to climate change will require concerted efforts by governments, businesses, and individuals around the world. This may include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and developing new technologies and infrastructure to help communities adapt to changing conditions.
Sun Damage
Sun damage is the term used to describe the negative effects that ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun has on the skin. This damage, which can result in a number of skin conditions and health problems, can happen even on cloudy or overcast days. Some of the most common effects of sun damage on the skin include:
-
Sunburn: Sunburn is a painful, red and sometimes blistering condition that occurs when the skin is exposed to too much UV radiation.
-
Premature aging: Exposure to UV radiation can cause the skin to age prematurely, leading to wrinkles, age spots, and a loss of elasticity.
-
Skin cancer: UV radiation is a leading cause of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
-
Eye damage: Exposure to UV radiation can also cause damage to the eyes, including cataracts and macular degeneration.
It is advised to limit sun exposure during peak hours, wear protective clothing and hats, and apply sunscreen with a high SPF rating on a regular basis to prevent sun damage. It is also important to regularly monitor the skin for changes, such as new or changing moles, and to seek medical attention if any concerning changes are noted. Treatment for severe sun damage may entail taking medication, having surgery, or undergoing other medical procedures. To create a successful treatment plan and to take action to stop future damage, it's critical to collaborate closely with a healthcare professional.
Poor Skincare
Poor skincare refers to the lack of proper hygiene and care for the skin. This can result in a number of skin conditions and problems, such as infections, dryness, acne, and premature aging. Some common examples of poor skincare habits include:
-
Infrequent washing: Failure to wash the face and body regularly can lead to a build-up of dirt, oil, and bacteria, which can cause acne, infections, and other skin conditions.
-
Harsh cleansing: Using harsh or abrasive cleansers and exfoliants can strip the skin of its natural oils and lead to dryness, irritation, and even injury.
-
Lack of moisturizing: Failure to moisturize the skin can lead to dryness, flakiness, and premature aging.
-
Excessive sun exposure: Overexposure to UV radiation from the sun can lead to sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
-
Poor nutrition: A diet lacking essential vitamins and minerals can impact the health of the skin, making it more prone to issues and conditions.
It's important to establish good skincare habits, such as washing the face and body frequently with mild, non-abrasive cleansers, moisturizing the skin to keep it hydrated, and protecting the skin from excessive sun exposure with sunscreen and protective clothing. Eating a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals can also help to support the health of the skin. In cases of skin issues or concerns, it is important to seek medical attention from a healthcare provider or dermatologist.
Over-Exfoliation
Over-exfoliation is the term for using exfoliating products or methods on the skin too frequently. This can cause rashes, inflammation, and damage to the skin's protective barrier. Exfoliation is the removal of dead skin cells from the skin's surface, which can help to clear clogged pores, sooth rough skin, and improve the texture of the skin. However, over-exfoliation can lead to a range of issues, including:
-
Dryness and irritation: Over-exfoliating can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness, redness, and flakiness.
-
Breakouts: Over-exfoliating can cause irritation and inflammation, which can lead to breakouts and acne.
-
Increased sensitivity: Over-exfoliating can make the skin more sensitive to other products and environmental factors, leading to further irritation and damage.
-
Premature aging: Over-exfoliating can damage the skin's natural barrier, leading to premature aging, fine lines, and wrinkles.
To avoid over-exfoliation, it is recommended to limit exfoliation to once or twice a week, depending on skin type and sensitivity. It's crucial to pick gentle exfoliating tools and methods over abrasive scrubs or mechanical exfoliants, such as using a mild chemical exfoliant or a brush with soft bristles. It is also important to listen to the skin's signals and adjust the frequency and intensity of exfoliation as needed. If irritation or other skin issues occur, it is important to stop exfoliating and seek the advice of a healthcare provider or dermatologist.
Dehydration
Dehydration is a state in which the body loses more water than it takes in, which can result in a variety of symptoms and health problems. Dehydration can also impact the health and appearance of the skin. When the body is dehydrated, it prioritizes the distribution of water to vital organs, which can leave the skin looking dry, dull, and tired. Dehydration can also cause the skin to become less resilient, making it more prone to fine lines and wrinkles. Some common signs of dehydration include:
-
Dry or flaky skin: Dehydration can cause the skin to lose its natural moisture, leading to dryness and flakiness.
-
Dark circles and puffiness: Dehydration can cause the blood vessels under the eyes to dilate, leading to dark circles and puffiness.
-
Fine lines and wrinkles: Dehydration can impact the skin's elasticity, making it more prone to fine lines and wrinkles.
-
Dull or tired-looking skin: Dehydration can cause the skin to look dull, tired, and lacking in radiance.
To prevent dehydration, it is important to drink plenty of fluids, especially water, and to avoid or limit alcohol and caffeine, which can dehydrate the body. Eating a diet rich in water-containing fruits and vegetables can also help to maintain hydration levels. To support the health of the skin, it is important to use moisturizers and hydrating products that help to lock in moisture and prevent water loss. If dehydration is severe or persistent, it is important to seek medical attention from a healthcare provider.
Nutrient Deficiencies
When the body is deficient in vital vitamins and minerals, it develops nutritional deficiencies. These nutritional deficiencies can cause a variety of health problems, including skin conditions. Some common nutrient deficiencies that can impact the health of the skin include:
-
Vitamin C: Vitamin C is essential for the production of collagen, a protein that supports skin health and elasticity. A deficiency in vitamin C can lead to dry, rough, and scaly skin.
-
Vitamin E: Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that helps to protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. A deficiency in vitamin E can lead to dry and irritated skin.
-
Vitamin D: Vitamin D is important for skin health, as it helps to regulate cell growth and repair. A deficiency in vitamin D can lead to dry, itchy, and flaky skin.
-
Zinc: Zinc is essential for the proper functioning of the skin's immune system and helps to support wound healing. A deficiency in zinc can lead to acne, rashes, and slow wound healing.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids are important for maintaining the health of cell membranes, which can impact the skin's moisture levels and elasticity. A deficiency in omega-3 fatty acids can lead to dry and inflamed skin.
Eating a balanced diet full of a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources is crucial to preventing nutrient deficiencies. In some cases, supplements may be recommended to address specific nutrient deficiencies. Use skincare products that contain nutrients that support skin health, such as vitamins C and E, to support the health of the skin. It is important to seek medical attention from a healthcare provider if nutrient deficiencies are thought to exist.
Stress
There are many ways that stress can affect the body, including the skin. The hormone cortisol, which is produced when the body is under stress, can cause inflammation and harm to the skin's natural barrier. Stress can weaken the immune system, which increases the risk of allergies, infections, and other problems with the skin. Some common ways that stress can impact the skin include:
-
Acne: Stress can cause an increase in oil production, leading to clogged pores and acne breakouts.
-
Eczema: Stress can trigger or exacerbate eczema, a condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
-
Psoriasis: Stress can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis, a condition that causes red, scaly patches on the skin.
-
Wrinkles: Stress can impact the skin's elasticity, making it more prone to wrinkles and fine lines.
-
Dryness: Stress can cause the skin to become dry and dehydrated, leading to flakiness and dullness.
To manage stress and support the health of the skin, it is important to prioritize self-care and stress-reduction techniques. This can include activities such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing, and getting enough sleep. It is also important to use skincare products that help to support the skin's natural barrier and avoid harsh or irritating products that can further damage the skin. If stress is persistent or severe, it is important to seek the advice of a healthcare provider or mental health professional.
Treating Flaky Skin
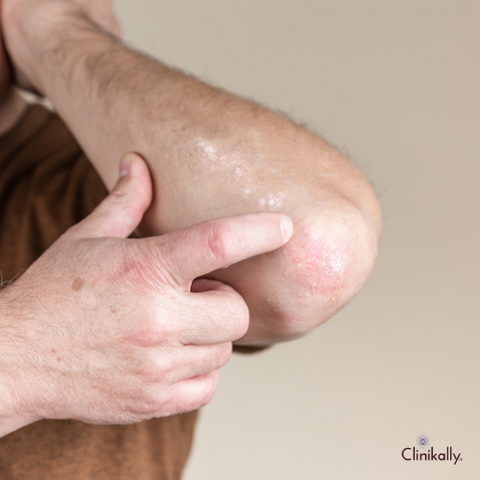
Flaky skin can be caused by a number of conditions, including dryness, eczema, psoriasis, and others. Flaky skin is typically treated with a combination of lifestyle changes and skincare products that soothe and hydrate the skin. Here are some tips for treating flaky skin:
-
Moisturize regularly: Moisturizing is key to help hydrate the skin and prevent flakiness. Look for a moisturizer that contains hydrating ingredients such as hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and ceramides.
-
Exfoliate gently: Exfoliating can help to remove dead skin cells and prevent flakiness, but it's important to do so gently to avoid further irritating the skin. Look for a gentle exfoliating product, such as a chemical exfoliant containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs).
-
Avoid hot showers: Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and flakiness. Try taking shorter, lukewarm showers instead.
-
Use a humidifier: Dry air can exacerbate flakiness, so using a humidifier can help to add moisture to the air and prevent dryness.
-
Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated is important for maintaining the health and hydration of the skin, so be sure to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
-
Consider using topical treatments: Depending on the underlying cause of the flakiness, topical treatments such as corticosteroid creams, antifungal creams, or prescription-strength moisturizers may be recommended by a healthcare provider.
It's important to note that if flaky skin is persistent or accompanied by other symptoms, it's important to seek the advice of a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Moisturizers
Moisturizers are skincare products that help to hydrate the skin and prevent dryness, flakiness, and other issues. There are many different types of moisturizers available, each with its own unique formulation and benefits. Here are some common types of moisturizers and their benefits:
-
Creams: Creams are thicker in consistency and are typically best for those with dry or very dry skin. They are formulated to provide long-lasting hydration and to create a barrier on the skin to prevent moisture loss.
-
Lotions: Lotions are lighter in consistency than creams and are typically best for those with normal to slightly dry skin. They absorb quickly into the skin and provide a more lightweight feel.
-
Serums: Serums are lightweight, fast-absorbing formulations that are typically applied before moisturizer. They are often formulated with active ingredients such as hyaluronic acid, vitamin C, or retinol, which can help to hydrate and improve the texture and appearance of the skin.
-
Oils: Face oils are becoming increasingly popular as a moisturizing option. They are typically lightweight and absorb easily into the skin, providing a natural-looking glow. Some common oils used in skincare include argan oil, jojoba oil, and rosehip oil.
When choosing a moisturizer, it's important to consider your skin type and specific concerns. For example, those with acne-prone skin may want to choose a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer, while those with very dry skin may benefit from a thicker, more emollient cream. It's also important to look for moisturizers that are formulated with ingredients that support the health of the skin, such as hyaluronic acid, ceramides, and niacinamide. These ingredients can help to improve hydration, protect the skin's barrier, and support overall skin health.
Ultimately, finding the right moisturizer may require some trial and error. It's important to choose a product that feels comfortable on the skin and provides the desired level of hydration and protection.
Exfoliation
Exfoliation is the process of removing dead skin cells from the surface of the skin. This can be done manually, using an exfoliating scrub or brush, or chemically, using products that contain alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs). Exfoliation can help to improve the texture and appearance of the skin, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and improve the absorption of other skincare products.
Here are some tips for safe and effective exfoliation:
-
Choose the right product: When choosing an exfoliating product, it's important to consider your skin type and specific concerns. Those with sensitive skin or acne-prone skin may benefit from a gentler exfoliating product, while those with thicker or oilier skin may benefit from a more intensive exfoliation.
-
Exfoliate once or twice per week: Over-exfoliating can damage the skin and cause irritation, so it's important to limit exfoliation to once or twice per week. This will allow the skin to regenerate and heal between treatments.
-
Be gentle: Whether using a physical exfoliant or a chemical exfoliant, it's important to be gentle and avoid scrubbing too hard. This can cause damage to the skin and lead to irritation and inflammation.
-
Follow with a hydrating product: After exfoliating, it's important to follow with a hydrating product, such as a moisturizer or serum. This will help to soothe and hydrate the skin, and prevent further irritation.
-
Avoid exfoliating if you have active breakouts: Exfoliating can further irritate active breakouts and lead to further inflammation and scarring. It's best to avoid exfoliating if you have active breakouts and instead focus on using gentle, non-irritating products to soothe and hydrate the skin.
Overall, exfoliation can be a beneficial addition to a skincare routine, but it's important to approach it with care and to choose the right products for your skin type and concerns.
Lifestyle Changes
Making positive lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on the health and appearance of your skin. Here are some lifestyle changes you can make to support healthy, radiant skin:
-
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help to keep the skin hydrated and healthy. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day, and more if you are exercising or in a hot climate.
-
Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are essential for healthy skin. Avoid processed and sugary foods, which can contribute to inflammation and skin problems.
-
Manage stress: Chronic stress can contribute to a variety of skin problems, including acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or therapy.
-
Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for healthy skin, as it allows the body to repair and regenerate skin cells. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
-
Protect your skin from the sun: Sun damage is a major contributor to premature aging and skin cancer. Wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30, seek shade during peak sun hours, and wear protective clothing, such as a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses.
-
Avoid smoking: Smoking can contribute to premature aging and skin damage. Quitting smoking can help to improve the health and appearance of your skin.
-
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help to improve circulation, boost the immune system, and reduce stress, all of which can benefit the health and appearance of your skin.
By making these positive lifestyle changes, you can help to support healthy, radiant skin, and improve your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
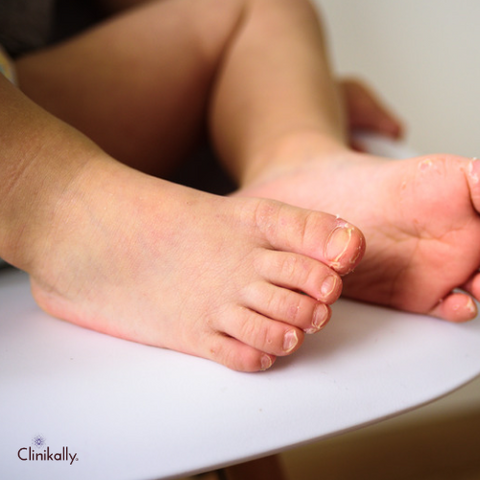
In conclusion, there are many factors that can contribute to flaky skin, including skin conditions, hormonal changes, climate, poor skincare, and lifestyle factors. However, there are also many treatments and strategies that can help to improve the health and appearance of the skin, such as moisturizers, exfoliation, hydration, and positive lifestyle changes. It's important to work with a healthcare professional to identify the underlying cause of flaky skin and develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and concerns. With the right care and attention, you can achieve healthy, radiant skin and improve your overall health and well-being.
































