Skin rashes can be uncomfortable, unsightly, and embarrassing, but they are also common and often treatable. In this blog, we will explore the common causes of skin rashes, treatment options, and how to prevent them through good skin care practices.
Causes of skin rashes

Skin rashes are caused by a variety of factors, including allergies, infections, and underlying medical conditions. The following are some common causes of skin rashes:
-
Infections, such as streptococcal and staphylococcal infections
-
Allergic reactions to substances, including medications, foods, and insect bites
-
Exposure to irritants, such as chemicals and plants
-
Chronic medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases and liver disease
-
Stress and anxiety
It is important to note that the exact cause of a skin rash can vary, and a healthcare professional, usually a dermatologist, can assist in determining the underlying issue. If a person has a persistent or severe rash, or if the rash is accompanied by other troubling symptoms, they should seek medical attention to ensure proper diagnosis and management.
Identifying Common Allergens in Skin Rash Development

Allergic reactions on the skin can result from several things. Some people are allergic to certain substances, which are known as allergens. It is important to take into account several allergy categories when determining common allergens linked to the development of skin rashes. The following common allergens can cause skin rashes:
-
Contact Allergens: Nickel is found in jewellery, belt buckles, and metal buttons. Latex is commonly found in gloves, elastic bands, and medical devices. Fragrances are used in perfumes, lotions, and cosmetic products. Cosmetics and personal care products contain preservatives such as parabens and formaldehyde.
-
Topical Medications: Some people may be allergic to topical medications like antibiotics, antifungals, or corticosteroids.
-
Plants: Poison ivy, oak, and sumac contain urushiol, which causes allergic reactions. Avoid touching nettle leaves as they can cause skin irritation. Some people may be allergic to certain flowers and plants.
-
Foods: Common food allergens include nuts, shellfish, dairy, and certain fruits. Some individuals may be sensitive to food additives such as colorings and preservatives.
-
Insect Bites and Stings: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to mosquito saliva. Tick bites may cause allergic reactions. Bee stings can cause allergic reactions, both locally and systemically.
-
Fabrics and Clothing: Chemicals and dyes are used in clothing manufacturing. Some individuals may have sensitivities to certain fabrics.
-
Metals: Cobalt and Chromium are found in metal alloys, including jewellery. Some individuals may be allergic to gold and silver.
-
Sunscreen Ingredients: Certain sunscreen ingredients may cause allergies in some people.
Identifying the specific allergen causing a skin rash often necessitates a detailed history, examination, and, in some cases, additional testing such as patch testing or blood tests. If someone has persistent or severe skin rashes, they should consult with a healthcare professional or allergist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the Role of Immune System in Skin Rashes
The immune system is important in the development of skin rashes, especially those caused by allergic reactions, infections, or autoimmune disorders. Here's an overview of how the immune system participates in various types of skin rashes:
-
Allergic Reactions: A type I hypersensitivity reaction, which occurs when the immune system overreacts to innocuous items (allergens) like pollen, specific foods, or drugs, is frequently the cause of allergic skin rashes. Histamines and other chemicals are released as a result, resulting in symptoms including swelling, itching, and redness. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies are produced by the immune system in reaction to allergens during allergic reactions. Histamine and other inflammatory chemicals are released when these antibodies bind to mast cells and basophils.
-
Infections: Infections can also cause skin rashes because they set off an immunological reaction. Invasion of the skin by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause inflammation and draw immune cells to the afflicted area. Immune cells that fight infectious pathogens include macrophages and neutrophils. The immune reaction itself may occasionally result in tissue damage and rash formation.
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks healthy cells and tissues in the body. In autoimmune skin conditions like psoriasis or lupus, the immune system's response leads to inflammation and the formation of skin lesions. In autoimmune skin disorders, an imbalance of cytokines, which are signaling molecules involved in immune responses, can contribute to the inflammatory process and skin rash development.
-
Contact Dermatitis: Contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. This type of reaction involves delayed hypersensitivity, where immune cells infiltrate the skin after exposure to the triggering substance. T-cells, a type of white blood cell, are often implicated in contact dermatitis. They play a role in the immune response and can contribute to rash formation.
Different forms of skin rashes
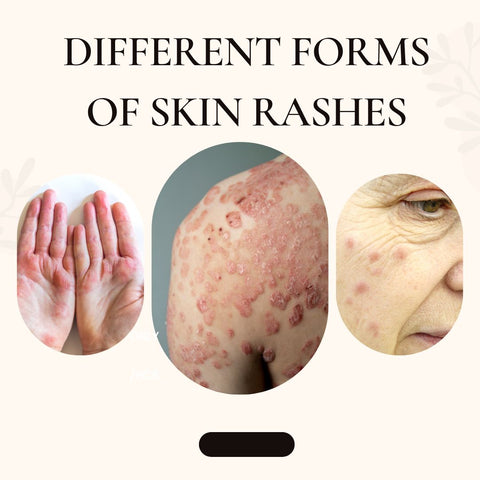
Skin rashes can take many different forms, and each type of rash may have its own unique set of symptoms and causes. Here are three of the most common types of skin rashes:
-
Eczema: This is a chronic condition that is characterised by itchy, red, and scaly skin.
-
Psoriasis: This is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes red, scaly patches on the skin.
-
Hives: Hives are raised, red, and itchy welts that can be caused by allergens or stress.
By understanding the different types of skin rashes, you can better identify your symptoms and find the right treatment to manage your skin rash. You can now get best online skin care consultation with leading dermatologists in India who will look into your underlying skin condition and recommend best treatment plans delivered directly to your doorstep only with your trusted digital clinic for skin & hair. Whether you are dealing with eczema, psoriasis, or hives, there are many options available to help you find relief and keep your skin healthy and vibrant.
Pediatric Skin Rashes: What Parents Should Know
Paediatric skin rashes are common and can be caused by a variety of factors, such as infections, allergies, and environmental exposure. Here's what parents should know about paediatric skin rashes:
-
Common Causes: Childhood rashes can be caused by viruses like chickenpox, measles, or roseola. Bacterial infections, such as impetigo and cellulitis, can cause rashes. Contact with allergens in the environment, certain foods, or medications can trigger rashes. A chronic condition characterised by dry, itchy skin that often begins in infancy. Blocked sweat ducts cause red, itchy bumps, especially during hot weather.
- Contact Dermatitis: ommon triggers include soaps, detergents, certain fabrics, and plants like poison ivy.
- Diaper Rash: Causes include prolonged exposure to wetness, friction, or sensitivity to nappy materials. Regular diaper changes, gentle cleansing, and the use of diaper creams.
- Insect Bites and Stings: Mosquito bites may cause red, itchy welts. Bee or wasp stings can cause localised swelling and redness.
- Heat-Related Rashes: Small red bumps caused by sweat trapped in sweat ducts, typically in skin folds.
- Fungal Infections: Candidiasis, also known as a yeast infection, can cause nappy rash and skin folds. A fungal infection causing a circular, red rash with a clear center.
- Pediatric Psoriasis: Psoriasis is less common in children and is characterised by red, scaly patches. Family history may be a contributing factor.
- When to Seek Medical Attention: Prolonged or worsening rash. Infection signs include pus, warmth, or red streaks. A high fever may accompany the rash. Severe allergic reactions can cause difficulty breathing and swallowing. Behaviour changes or signs of dehydration.
- Home Care: Keep the affected area clean and dry. Use mild soaps and avoid harsh detergents. Apply moisturisers for conditions like eczema. Administer any prescribed medications as directed.
-
Professional Evaluation: If a rash persists, worsens, or is associated with other concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare professional, typically a paediatrician or dermatologist.
In addition to practicing excellent skin hygiene and being watchful, parents should also visit a doctor if they have any concerns about a skin rash. A medical expert can offer a precise diagnosis, suggest the best course of action, and, if necessary, arrange for additional testing.
Seasonal Skin Rashes and Care
Seasonal changes can have an impact on the skin, causing a variety of issues. Here's a guide to seasonal skin rashes with care tips:
-
Winter Skin Rashes: Dry skin can be caused by cold air and low humidity levels. Use a humidifier, moisturise frequently, and avoid hot showers. Cold weather can worsen eczema flare-ups. Moisturise frequently, use gentle cleansers, and dress in layers to avoid overheating.
-
Summer Skin Rashes: Sweating in hot weather can result in prickly heat. Wear loose, breathable clothing to stay cool. Prolonged exposure to the sun can cause redness and pain. Apply sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and seek shade.
-
Fall Skin Rashes: Exposure to allergens like poison ivy is common. Learn to identify irritants, and wear protective clothing when outdoors.
-
Spring Skin Rashes: Pollen allergies can cause skin reactions. Shower after spending time outdoors, keep windows closed, and use antihistamines as needed.
General Skin Care Tips:
-
Moisturise: Keep your skin hydrated all year round. Choose a moisturiser that is appropriate for your skin type.
-
Sun Protection: Even on cloudy days, apply sunscreen with SPF. Reapply every 2 hours, more frequently if swimming or sweating.
-
Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep the skin hydrated from within.
-
Gentle Cleansing: Avoid using harsh cleansers that strip the skin of its natural oils.
-
Avoid Irritants: Identify and avoid substances that cause allergies or skin irritations.
-
Dress appropriately: Wear weather-appropriate clothing to protect your skin from harsh conditions.
-
Healthy Diet: For overall skin health, consume a well-balanced diet high in vitamins and antioxidants.
-
Allergy Management: If you have seasonal allergies, treat them with the proper medications and precautions.
Adapting a Skincare Routine:
-
Adjust your skincare routine according to the season. For example, use a thicker moisturiser in the winter and a lighter one in the summer.
Holistic Approach:
-
Consider stress, diet, and lifestyle, as all of these can have an impact on skin health. Consider a holistic approach to skincare.
By being aware of seasonal changes and implementing proper skincare practices, you can help prevent and manage seasonal skin issues. If you have specific concerns or conditions, consulting a healthcare professional, particularly a dermatologist, can provide tailored guidance.
Preventing skin rashes: A proactive approach
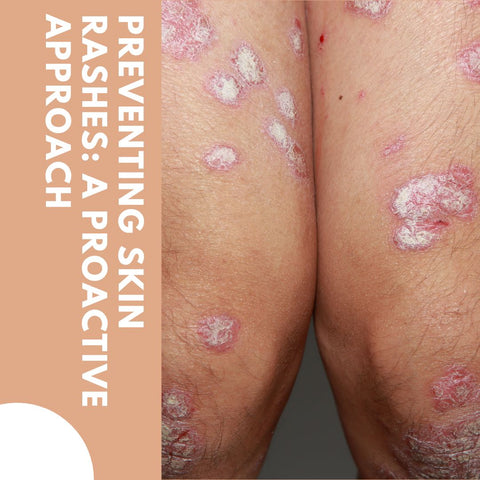
Preventing skin rashes is an important aspect of overall skin health. By taking a proactive approach to skin care, you can reduce your risk of developing skin rashes and keep your skin looking and feeling its best. Here are two key strategies for preventing skin rashes:
-
Good skin care practices: Taking good care of your skin is essential for preventing skin rashes. This includes keeping your skin clean and moisturized, as well as protecting it from harsh weather conditions.
-
Avoiding triggers: Some people may experience skin rashes as a result of certain triggers, such as certain foods or irritants. By avoiding these triggers, you can reduce your risk of developing skin rashes.
By following these preventive strategies, you can help keep your skin healthy, protected against skin rashes, and looking and feeling its best.
The importance of diet and nutrition for skin rash management
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in the health of your skin. What you eat can impact the severity and frequency of skin rashes, and making the right dietary choices can help you manage these symptoms. Here are a few ways in which diet and nutrition can impact skin rashes:
-
Eliminating trigger foods: Certain foods can trigger skin rashes in some individuals. By identifying and eliminating these trigger foods, you can reduce your symptoms.
-
Boosting skin health: Consuming a diet rich in vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, vitamin E, and zinc can improve the overall health of your skin and reduce the likelihood of rashes.
-
Managing inflammation: Foods with anti-inflammatory properties, like leafy greens, fatty fish, and turmeric, can help reduce skin inflammation and manage skin rash symptoms.
-
Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep your skin hydrated and prevent skin rashes from becoming dry and irritated.
By incorporating the right foods and drinks into your diet, you can help manage and prevent skin rashes, and keep your skin looking and feeling its best.
Expert Tips for Skin Rash Care and Prevention
Caring for and preventing skin rashes involves a combination of good skincare practices, identifying triggers, and, in some cases, seeking professional advice. Here are expert recommendations for skin rash treatment and prevention:
Skin Rash Care:
-
Keep the Area Clean: Gently clean the affected area with mild, fragrance-free soap and lukewarm water. Avoid using hot water because it can irritate the skin even more.
-
Avoid Scratching: Resist the urge to scratch, as this can aggravate the rash and lead to infection. Keep your nails short to prevent damage.
-
Apply Moisturiser: To keep the skin hydrated, use a hypoallergenic, fragrance-free moisturiser. Apply it frequently, especially after bathing.
-
Cold Compress: Use a cold compress to reduce inflammation and relieve itching. Wrap ice in a cloth instead of applying it directly to the skin.
-
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Creams: Over-the-counter creams containing hydrocortisone may help with certain rashes. However, consult a healthcare professional before use.
-
Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can reduce itching. Consult a healthcare professional for the appropriate dosage.
-
Avoid Irritants: Identify and avoid substances that may trigger or worsen the rash, such as harsh soaps, fragrances, or certain fabrics.
Skin Rash Prevention:
-
Identify Triggers: If you have recurring rashes, look for potential triggers, such as certain foods, skincare products, or environmental factors.
-
Allergy Management: If allergies are contributing to your skin rash, treat them with medications and preventative measures. Consult an allergist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
-
Dress appropriately: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing, particularly in hot and humid weather. Avoid wearing tight clothing, which can trap moisture and irritate your skin.
-
Sun Protection: To protect your skin from the sun's harmful effects, apply sunscreen with a high SPF. Reapply as needed, particularly after swimming or sweating.
-
Hydration: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Proper hydration supports overall skin health.
-
Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques, as stress can exacerbate certain skin conditions. Consider activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
-
Avoid Environmental Triggers: Be mindful of environmental factors that may trigger skin rashes, such as exposure to certain plants, chemicals, or insects.
-
Regular Skincare Routine: Establish a consistent skincare routine with products suitable for your skin type. Be cautious when trying new products, and patch-test before full application.
-
Consult a Dermatologist: If you have persistent or severe skin rashes, or if you are unsure about the cause, consult a dermatologist for a thorough evaluation and personalised advice.
-
Review Medications: Some medications may cause skin reactions. If you suspect a drug-related rash, consult your healthcare provider for potential alternatives.
Taking a proactive approach to skincare, identifying triggers, and seeking professional advice when needed are essential components of effective skin rash care and prevention. Individualised care based on the specific nature of the rash and its underlying causes is crucial for optimal outcomes.
Distinguishing between a minor skin rash and a serious condition
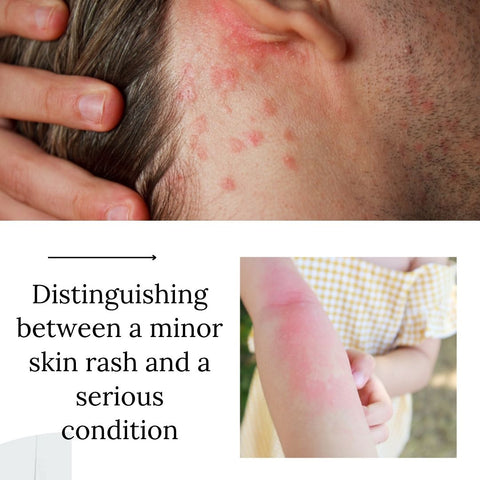
When it comes to skin rashes, it can be difficult to determine whether a rash is a minor issue or a more serious concern. Here are some guidelines to help you distinguish between the two:
-
Look for additional symptoms: If a rash is accompanied by fever, difficulty breathing, or swelling, it may be a sign of a more serious condition and requires medical attention.
-
Consider the timing and progression of the rash: A sudden, severe rash that spreads rapidly may be indicative of a serious condition.
-
Take note of any previous skin conditions: If you have a history of skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, a rash may be related to these conditions and require medical treatment.
-
Pay attention to pain levels: A painful rash that is accompanied by blisters or open sores may be indicative of a more serious condition.
If you are uncertain whether a rash is serious, it is always best to seek medical advice. By understanding the signs of a minor skin rash and a more serious condition, you can take the appropriate steps to protect your health and keep your skin looking and feeling its best.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Rashes
While many rashes can be treated at home with care, there are some cases where medical attention is required. Here are some guidelines on when to consult a healthcare professional about a rash:
-
Severe Symptoms: If the rash is accompanied by severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or other signs of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), seek emergency medical care right away.
-
Fever: If the rash is accompanied by a fever, particularly in children, it may indicate an underlying infection requiring medical attention.
-
Painful Rashes: Rashes that are extremely painful or cause discomfort beyond what can be treated with over-the-counter medications may necessitate medical attention.
-
Blisters or Ulcers: Consult a healthcare professional if your rash includes blisters, open sores, or ulcers, especially if there is pus or signs of infection.
-
Widespread Rash: If the rash is widespread, covering a large area of the body, or spreading rapidly, it may require medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
-
Persistent or Recurrent Rashes: If a rash lasts more than a few days, worsens, or returns repeatedly, seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
-
Change in Behavior or Systemic Symptoms: If the person with the rash has other systemic symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or dizziness, or if their behaviour changes, this may indicate an underlying problem that requires medical attention.
-
Signs of Infection: If the rash shows signs of infection such as redness, warmth, swelling, or if there's discharge or oozing, medical attention is necessary.
-
Unknown Cause: If you are unsure about the cause of the rash, or if it is related to a new medication or exposure, see a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
-
Concerns for Serious Conditions: If you are concerned about the possibility of a serious underlying condition, such as an autoimmune disorder, or if you have a family history of specific skin conditions, you should see a dermatologist or other healthcare professional.
Remember that every person and rash is different, and these guidelines are general. If you have concerns about a rash, you should trust your instincts and seek medical attention. If in doubt or if the rash is causing significant discomfort or worry, it's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and guidance.
Skin Rash Myths and Facts
Skin rashes are frequent, and many myths and beliefs accompany their prevalence. To better understand and treat skin diseases, it's critical to distinguish fact from myth. Following are some typical misconceptions and truths regarding skin rashes:
-
Myth: All rashes are contagious.
-
Fact: Not all rashes are contagious. While some diseases, such as infections, can be transmitted through direct contact, many others, such as eczema or psoriasis, are not contagious and are caused by internal processes.
-
Myth: Rashes only appear in certain parts of the body.
-
Fact: Rashes can appear anywhere on the body, including the face, arms, legs, and torso. The cause of a rash often determines its location and appearance.
-
Myth: All rashes are itchy.
-
Fact: Although itching is a common symptom of many rashes, not all of them are itchy. Some may result in pain, burning, or no discomfort at all.
-
Myth: Only children develop rashes.
-
Fact: Rashes can affect people of any age. Some rashes, such as nappy rash, are more common in babies, but adults can develop a variety of skin conditions.
-
Myth: Scratching a rash causes it to heal faster.
-
Fact: Scratching a rash can aggravate the condition, lead to infection, and delay healing. It's important to resist the urge to scratch and instead follow appropriate care measures.
-
Myth: All rashes are an allergic reaction.
-
Fact: Several factors, including irritants, autoimmune diseases, infections, and genetics, can cause rashes. An allergic response is merely one type of trigger.
-
Myth: Prescription medications are necessary for all rashes.
-
Fact: Antihistamines, moisturisers, and over-the-counter creams can be used to treat a lot of rashes. Some, however, may necessitate the use of prescription medications, particularly if the symptoms are severe or caused by an underlying medical condition.
-
Myth: Natural remedies treat all rashes.
-
Fact: While some natural remedies may help with certain rashes, they are not always effective. It is critical to determine the specific cause of the rash and select appropriate treatments.
-
Myth: Rashes always indicate a serious health issue.
-
Fact: While some rashes may be associated with serious conditions, many are benign and can be easily treated. Consulting a healthcare professional can assist in determining the cause and the best course of treatment.
-
Myth: Rashes always look the same.
-
Fact: There are many different types of rashes, such as redness, bumps, blisters, scales, and more. Different skin conditions present differently, so a precise diagnosis is crucial.
-
Myth: A rash will not return once it has cleared up.
-
Fact: Rashes can recur, particularly those caused by long-term illnesses like psoriasis or eczema. Managing underlying causes and maintaining a consistent skincare regimen can help prevent flare-ups.
If you have a persistent or concerning rash, see a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. Avoid self-diagnosis and follow evidence-based practices for optimal skin health.
Take control of your skin rashes today
In conclusion, skin rashes can be caused by a variety of factors and can range from mild to severe. Treatment options include topical creams, prescription medications, and lifestyle changes, and prevention can be achieved through good skin care practices and avoiding known triggers. Different types of skin rashes, such as eczema, psoriasis, and hives, can be managed through a balanced diet and the use of natural remedies. Stress can also play a role in skin rashes, making it important to manage stress levels. If a rash is accompanied by serious symptoms, or does not improve with topical treatments, it is important to see a doctor. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for skin rashes, you can take steps to manage and prevent them, and keep your skin looking and feeling healthy.
Treatment options for skin rashes
Skin rashes are treated according to their underlying cause. It is important to note that self-diagnosis and self-treatment may not always be effective, so it is best to consult a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. However, below are some general treatment options for common types of skin rashes:
-
Creams and ointments, such as hydrocortisone cream and calamine lotion
-
Prescription medications, such as antibiotics and antihistamines
-
Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers and using mild soaps and moisturisers
Always follow healthcare professionals' advice and prescriptions. Additionally, it is critical to communicate any concerns or changes in the rash during treatment.
The use of natural remedies for skin rashes
Sometimes, natural therapies can help relieve small skin rashes, and they can also be used in conjunction with conventional treatments. It's crucial to remember that not all natural therapies have scientific backing, and there can be variation in their effectiveness. It's best to speak with a healthcare provider to make sure a natural therapy is safe and suitable for the particular illness before attempting it, especially for severe or persistent rashes. The following are some typical natural treatments for skin rashes:
-
Aloe vera: a plant known for its soothing and moisturising properties
-
Tea tree oil: an essential oil with antifungal and antibacterial properties
-
Other natural remedies, such as chamomile and oatmeal baths, can also provide relief
Natural remedies may provide relief to some people, but their efficacy varies. It is critical to approach them with caution, especially when dealing with skin issues. If you have any concerns about a rash or if it persists, see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Technology and Innovations in Treating Skin Rashes
Technological developments have produced creative methods for treating a range of skin issues, including rashes. These technological advancements seek to increase therapy efficacy, improve diagnosis, and deliver more individualised care. The following are some noteworthy advances in technology and new approaches to treating skin rashes:
-
Telemedicine and Dermatology Apps: Patient consultations with medical specialists can be conducted remotely through telemedicine platforms and dermatology applications. Dermatologists can evaluate skin rashes via online consultations, giving clients prompt access to professional guidance.
-
Teledermoscopy: Teledermoscopy involves sending high-resolution images of skin lesions for remote dermatologist evaluation. This can aid in the diagnosis of skin rashes and the early detection of potential issues.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Dermatology: AI algorithms analyse images and data to assist in diagnosing skin conditions. AI can improve accuracy in identifying patterns associated with various rashes, aiding healthcare professionals in making more informed decisions.
-
3D Printing for Customised Topical Treatments: 3D printing technology allows for the development of personalised topical treatments that are tailored to a patient's specific skin needs. This can enhance the effectiveness of medications and reduce adverse reactions.
-
Smart Wearables for UV Exposure Monitoring: UV-enabled wearables can monitor sun exposure and provide users with real-time data. This technology helps individuals manage their sun exposure to prevent conditions like sunburns and photosensitive skin rashes.
-
Microneedle Patches for Drug Delivery: Microneedle patches deliver medications via tiny needles that penetrate the skin's top layers. These patches can be designed to release specific drugs, allowing for more targeted treatment of skin conditions.
-
Light Therapy Devices: Handheld or at-home light therapy devices, such as LED masks, are available to treat psoriasis and acne. These devices target skin issues by using specific light wavelengths.
-
Electronic Skin Patches for Monitoring: Flexible electronic skin patches can monitor a variety of physiological parameters, such as hydration and temperature. These patches can provide useful information for people dealing with skin conditions.
-
Nanotechnology in Topical Treatments: Nanotechnology enables the creation of nanoscale drug delivery systems. Nano-sized particles can improve medication penetration and effectiveness in treating skin rashes.
-
Gene Therapy for Chronic Skin Conditions: Research in gene therapy aims to address underlying genetic factors contributing to chronic skin conditions. This innovative approach may offer long-term solutions for certain skin rashes.
Challenges and Considerations:
-
While these technologies show promise, they face challenges such as regulatory approval, cost, and availability.
-
Privacy and security are critical considerations when using digital health technologies and storing patient data.
-
Technological advancements should supplement, not replace, healthcare professionals' expertise in diagnosing and treating skin conditions.
Incorporating these technological advancements into dermatological practice has the potential to improve patient outcomes, improve diagnostics, and provide more personalised and effective treatments for various skin rashes. As technology continues to evolve, it's important to balance innovation with ethical considerations and evidence-based practices in dermatology.
The link between stress and skin rashes
Stress can affect or worsen a variety of skin diseases, and there is a complex association between stress and skin rashes. Stress is known to impair immunological function, set off inflammatory reactions, and throw off the hormone balance, all of which can exacerbate or cause skin problems. The following are some typical ways that stress affects the skin:
-
Stress can trigger or worsen skin rashes, making it important to manage stress through activities such as meditation and exercise
Improving skin health and controlling or preventing stress-related skin problems can be greatly aided by addressing the underlying stress and utilising efficient stress management techniques. Seeking advice from medical professionals is crucial for a thorough and customised approach to care if a patient has skin issues in addition to chronic stress.
Skin Rash First Aid Tips
Treating a skin rash with first aid entails acting quickly to reduce symptoms, stop more irritation, and encourage healing. Remember that these are only broad recommendations, and depending on the kind and intensity of the rash, it's important to speak with a healthcare provider for particular advice. For common skin rashes, consider the following first aid advice:
-
Gently clean the rash with a mild, fragrance-free soap and lukewarm water. Avoid hot water, as it can further irritate the skin.
-
Keep nails short to minimize damage and avoid scratching. Scratching can worsen the rash and potentially lead to infection.
-
Apply a hypoallergenic and fragrance-free moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated. This is particularly important for conditions like eczema.
-
Apply a cold compress to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and soothe itching. Avoid using ice directly on the skin; wrap it in a cloth.
-
For certain rashes, over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams may provide relief. However, use them as directed and consult a healthcare professional if necessary.
-
If itching is a significant symptom, oral antihistamines can help control it. Follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional if needed.
-
If possible, identify and avoid substances or conditions that trigger or worsen the rash, such as certain fabrics, soaps, or allergens.
-
Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing to prevent further irritation. Avoid tight clothing that can trap moisture.
-
Staying well-hydrated supports overall skin health and can contribute to the healing process.
-
Give the affected area time to heal by avoiding activities or conditions that may exacerbate the rash.
When To Seek Professional Help:
-
If the rash is severe, persists, or worsens.
-
If there are symptoms of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus.
-
If the rash is associated with systemic symptoms such as fever or difficulty breathing.
-
If the cause of the rash is unknown or if self-treatment does not work.
Keep in mind that these first aid suggestions are broad guidelines. It is imperative to seek guidance from a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, regarding the precise type and origin of the rash. In the event that the rash does not go away or if you are concerned about its severity, you should get medical help right once.
Disclaimer
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
































