Skin-related psoriasis is a persistent autoimmune disorder that results in red, scaly patches. Although over-the-counter (OTC) medications can be helpful in controlling mild to moderate psoriasis symptoms, some individuals may discover that these medications are insufficient. In such circumstances, it is crucial to be aware of the warning indications that more extensive therapy is required and to look for suitable alternatives. If the symptoms do not change or worsen after trying OTC therapies for psoriasis for a number of weeks, this could be a sign that they are ineffective. For instance, if you have been applying a topical corticosteroid cream to lessen itch and inflammation but the psoriasis plaques are still there or are getting worse, the cream may not be working to control your symptoms. Another indication is if your quality of life is being negatively impacted, your everyday activities are being hindered, or the psoriasis patches are getting more painful or uncomfortable. For instance, over-the-counter medications might not be effective in treating symptoms of psoriasis if they include joint discomfort, stiffness, or intense itching.
There are a number of options to take into account when over-the-counter psoriasis treatments are insufficient. A dermatologist is one option who can evaluate your symptoms and suggest more intense treatments like prescription-strength topical medicines or oral medications. Vitamin D analogues, oral retinoids, and topical calcineurin inhibitors are a few examples of prescription drugs for psoriasis. Consider light treatment, which includes exposing the damaged skin to UV light, as an additional remedy. With a prescribed light box, light therapy can be carried out at home or in a dermatologist's office.
Understanding OTC Psoriasis Treatments
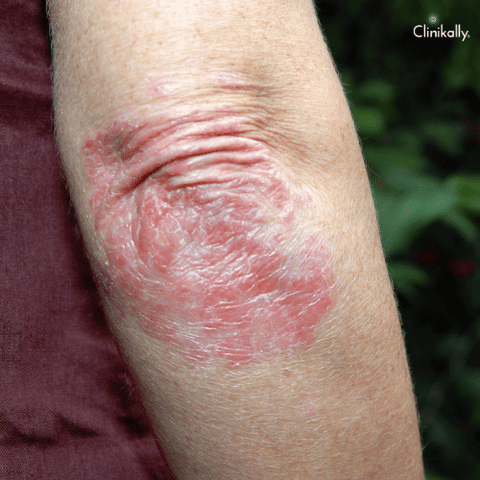
Skin-related psoriasis is a persistent autoimmune disorder that results in red, scaly patches. There are numerous over-the-counter (OTC) psoriasis medications available, and they all function differently to help lessen the condition's symptoms. Topical corticosteroids are one sort of over-the-counter medication for psoriasis. These drugs function by lowering inflammation and irritation when administered directly to the skin. They can be used to treat mild to moderate psoriasis for brief periods of time and come in various strengths.
Coal tar, which can be found in shampoos, soaps, and lotions, is another OTC remedy for psoriasis. The way coal tar works is by lessening inflammation and delaying the proliferation of skin cells. Another popular component in over-the-counter psoriasis remedies is salicylic acid. By encouraging the shedding of dead skin cells, it aids in the removal of scales and the smoothing of rough skin. Moisturisers, bath additives, and vitamin D, and fish oil are some additional over-the-counter (OTC) psoriasis remedies. These remedies could aid in healing, reducing inflammation, and soothing the skin.
Although over-the-counter (OTC) psoriasis treatments can be successful for some people, they might not be successful for everyone. The importance of speaking with a dermatologist for additional treatment options should not be underestimated if you have severe psoriasis or if your symptoms do not get better with over-the-counter medications.
Topical Medications for Psoriasis
One of the most popular over-the-counter (OTC) therapies for psoriasis is topical medicine. They function by lowering inflammation, inhibiting skin cell development, and reducing itchiness and scaling. Among the most popular topical treatments for psoriasis are:
-
Corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory drugs that can lessen scaling, itching, and redness. They come in various strengths and can be applied directly to the skin's afflicted areas.
-
Salicylic acid: This medication works by speeding up the shedding of the skin's outer layer, which helps to lessen scaling and encourages the development of new skin cells.
-
Coal tar: A by-product of coal that has been used to treat psoriasis for centuries. It works by slowing the growth of skin cells and reducing inflammation.
-
Vitamin D analogues: These medications are synthetic versions of vitamin D that work by slowing the growth of skin cells and reducing inflammation.
-
Topical retinoids: These are medications derived from vitamin A and can help reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells.
While these drugs can be successful in treating psoriasis, it is important to remember that they may also have unwanted effects like skin irritation, skin thinning, and increased sensitivity to sunlight. Before utilising any over-the-counter psoriasis medication, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider.
How OTC Treatments Work and Their Limitations
OTC psoriasis therapies work by easing itching and scaling, lowering inflammation, and inhibiting the proliferation of skin cells. These medications frequently include active substances like corticosteroids, coal tar, or salicylic acid. OTC remedies do have their limitations, though. For severe cases or all forms of psoriasis, they might not be beneficial. Additionally, these medications may cause side effects or allergic reactions in some people. Before beginning any over-the-counter (OTC) psoriasis treatment, it is crucial to speak with a healthcare provider to ensure that it is suitable and safe for your condition. If over-the-counter remedies don't work, a doctor may prescribe stronger drugs or suggest alternative therapies like phototherapy or biological therapy.
Recognizing Signs of Treatment Failure
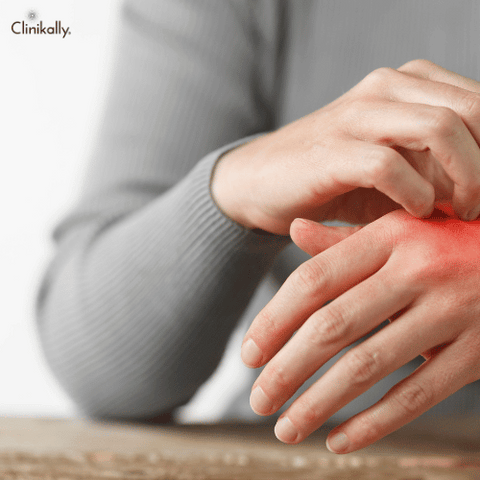

Although many psoriasis sufferers can control their symptoms with over-the-counter (OTC) medications, some people may discover that these treatments are ineffective for their condition. OTC psoriasis medications that are not working include:
-
No improvement in symptoms: It might be time to try a different strategy if you've been using an over-the-counter medication for psoriasis for a number of weeks and haven't noticed any relief from your symptoms.
-
Symptoms getting worse: If your psoriasis symptoms are getting worse while taking an OTC medication, this may indicate that the medication is ineffective or that your condition has gotten worse and is now more severe.
-
Skin irritation or allergic reactions: Some over-the-counter psoriasis treatments have the potential to cause skin irritation or allergic reactions. If you experience any of these side effects, you should discontinue the use of the medication and consult with your doctor.
-
Pain or discomfort: Psoriasis can be painful, but if you experience pain or discomfort while using an over-the-counter treatment, it may not be the best option for you.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should consult your doctor about other psoriasis treatment options.
Common Symptoms of Psoriasis Flare-Ups
An inflammatory disease that affects the skin, psoriasis causes red, scaly patches to appear on various parts of the body. Depending on the type of psoriasis a person has, the symptoms of a flare-up might vary, but frequent symptoms include:
-
Skin patches that are red and covered in thick, silvery scales
-
Skin that is dry and cracked and may bleed or itch
-
The affected areas may experience burning or soreness.
-
Nails that are thickened, ridged, or pitted
-
Joint swelling or stiffness
Because psoriasis is a chronic condition, symptoms may appear and disappear over time. However, it might be a sign of treatment failure if someone's psoriasis symptoms do not get better with over-the-counter remedies or if their condition gets worse. For a full evaluation and treatment options, they should see a dermatologist.
When OTC Treatments Are No Longer Effective
If your psoriasis symptoms are not improving or worsening with over-the-counter medications, you should see a dermatologist for further evaluation and treatment. Following are some indicators that your psoriasis may be getting worse or not responding to over-the-counter medications:
-
Increasing redness and inflammation: If the affected skin becomes redder and more inflamed, or if the patches grow larger, it could mean that the psoriasis is worsening.
-
Scaling and flaking: If the skin becomes more dry, scaly, and flaky, or if the scales become thicker and more difficult to remove, psoriasis may be resistant to treatment.
-
Itching and discomfort: If your psoriasis is causing you more itching or discomfort than usual, or if it is interfering with your daily activities, this could be an indication that the condition is worsening.
-
Joint pain and stiffness: If you have joint pain and stiffness in addition to your psoriasis, you may have psoriatic arthritis, which requires more aggressive treatment.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Seeking Professional Help for Psoriasis
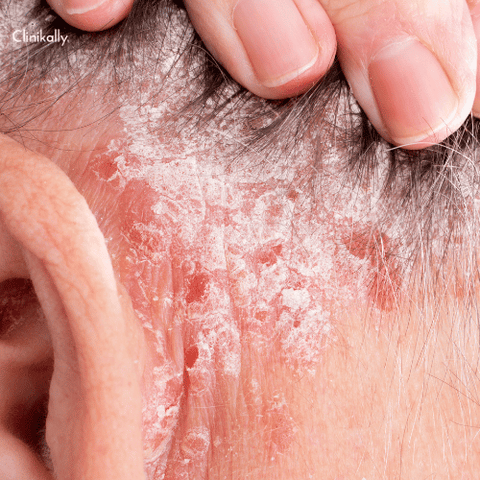
It could be necessary to seek professional assistance if over-the-counter (OTC) medications for psoriasis are ineffective or if the condition is severe. Dermatologists can diagnose psoriasis and provide specific treatment recommendations. Here are some indicators that it might be time to consult a professional:
-
Worsening symptoms: If your psoriasis symptoms are worsening despite using OTC treatments, it's time to seek professional help.
-
Large or widespread patches: If psoriasis patches are large or widespread, it may be difficult to treat them effectively with over-the-counter medications.
-
Joint pain: Psoriasis can cause pain and inflammation in the joints. If this occurs, a dermatologist may need to collaborate with a rheumatologist to devise a treatment plan.
-
Emotional distress: Psoriasis is a distressing condition that can have a negative impact on a person's emotional well-being. If your psoriasis is causing you emotional distress, you should seek professional help.
-
Other medical conditions: Psoriasis is linked to other medical conditions such as diabetes and heart disease. If a person has other health conditions, it is critical to collaborate with a healthcare team to effectively manage all of the conditions.
A dermatologist can assess a patient's psoriasis symptoms and suggest the best course of treatment, which may entail using prescription drugs, phototherapy, or other cutting-edge procedures. It is crucial to closely adhere to the dermatologist's advice and to express any concerns or problems that develop throughout treatment.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
If you are experiencing severe psoriasis symptoms or if OTC treatments have not improved your condition, it is time to see a dermatologist. Here are some specific situations in which you should consult a dermatologist:
-
Your psoriasis has spread rapidly or covers a large portion of your body.
-
You are experiencing joint pain or swelling.
-
Psoriasis is interfering with your daily life or causing emotional distress.
-
Your skin is extremely dry, cracked, or bleeds.
-
You've picked up a secondary infection.
-
Your current treatment is causing side effects for you.
A dermatologist can identify your psoriasis, evaluate its severity, and suggest the best course of action based on your particular requirements. They can also keep track of your development and modify your treatment strategy as necessary.
Diagnosis and Treatment Planning with a Dermatologist
It's time to see a dermatologist if you suspect that OTC medications for your psoriasis are no longer working. The dermatologist will examine you physically, go over your health history, and inquire about your symptoms. Along with your current medications, the doctor will inquire about any allergies you may have. The dermatologist will collaborate with you to create a treatment plan if they determine that you have psoriasis. Your treatment strategy may involve a combination of topical drugs, oral medications, biological therapies, or phototherapy, depending on the kind and severity of your psoriasis.
The dermatologist could also advise making lifestyle modifications to help control your symptoms. This may involve a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress reduction methods, and a reduction in triggers that may lead to flare-ups. Attend all follow-up appointments and strictly adhere to your dermatologist's treatment regimen. Remember to talk to your dermatologist if you have any adverse effects or have questions regarding your therapy. To help you better manage your symptoms, they can change your treatment strategy.
Treating Psoriasis with Prescription Medications
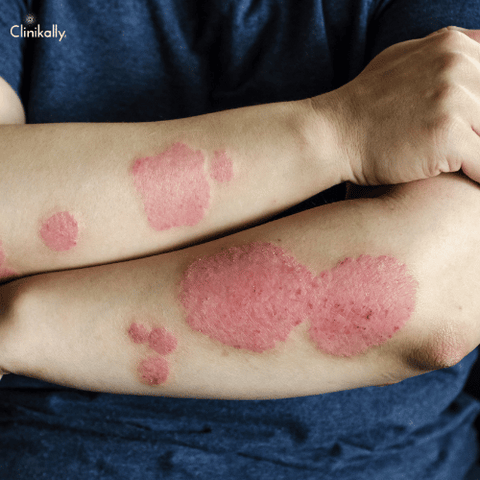

A persistent inflammatory condition known as psoriasis affects the skin and can cause red, scaly patches to develop on different parts of the body. A dermatologist may recommend prescription drugs when over-the-counter remedies are ineffective. Psoriasis can be treated with a number of different prescription drugs, including:
-
Topical corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory drugs that are rubbed onto the skin's surface in the affected area. They typically treat mild to moderate psoriasis and function by lowering inflammation and inhibiting the development of new skin cells.
-
Topical vitamin D analogues: These are artificial vitamin D formulations that are applied topically. They function by reducing swelling and slowing the growth of skin cells.
-
Topical retinoids: These are vitamin A derivatives that can help reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells.
-
Coal tar preparations: A by-product of coal processing, coal tar has been used for treating psoriasis for centuries. It works by reducing inflammation and slowing the growth of skin cells.
-
Systemic medications: Systemic medications may be prescribed for moderate to severe cases of psoriasis. These drugs work throughout the body to reduce inflammation and slow the growth of skin cells and can be administered orally or intravenously. Examples include biologic medications, cyclosporine, and methotrexate.
Remember that these drugs may have side effects and that they should only be used under a dermatologist's supervision. Additionally, the effectiveness of these drugs may differ from person to person and from case to case, depending on the degree of psoriasis. Before progress is noticed, it can take several weeks or even months of treatment.
Topical and Oral Prescription Medications for Psoriasis
For the treatment of psoriasis, a number of prescription drugs, both topical and oral, are offered. Among the topical treatments for psoriasis are:
-
Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that are commonly used to treat psoriasis. They help to reduce redness, itching, and inflammation.
-
Topical retinoids are vitamin A derivatives that slow the rate of skin cell proliferation, which results in psoriasis plaques.
-
Vitamin D analogues are synthetic forms of vitamin D that help to reduce inflammation by slowing the growth of skin cells.
-
Calcineurin inhibitors are topical immunosuppressants that help to reduce inflammation and protect healthy skin cells from immune system attacks.
Oral psoriasis medications include:
-
Methotrexate: This drug suppresses the immune system and can help to lessen inflammation and slow the development of new skin cells.
-
Cyclosporine: This drug, which is also an immunosuppressant and can be used to treat severe psoriasis, has some serious drawbacks, so it's typically only prescribed for brief periods of time.
-
Biologics: These medications, which are created from living cells, target particular immune system components that are involved in psoriasis. Biologics are typically used to treat severe psoriasis cases that have not responded to other therapies.
-
Apremilast: A newer oral medication that works by inhibiting specific enzymes involved in the inflammatory process.
Working with a dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment for your specific case of psoriasis is critical, as treatment will vary depending on the severity and location of your psoriasis, as well as other factors such as your overall health and any other medications you may be taking.
Biological Treatments for Severe Psoriasis
A type of medication known as a biologic treatment works by specifically targeting immune system parts that are responsible for psoriasis. They are often used only in moderate to severe psoriasis cases that have not responded to previous therapies. Biologics, which are frequently administered via injection or infusion, work to treat psoriasis by inhibiting the activity of specific immune cells or proteins implicated in the onset of the disease. Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, ustekinumab, and secukinumab are some of the biologics that are frequently used to treat psoriasis.
In addition to being more expensive than other psoriasis drugs, biologic therapy may also have a higher risk of infection, including deadly infections like TB. Because of this, they are typically only prescribed to individuals who have tried other treatments without success or who have severe psoriasis that is seriously affecting their quality of life. Patients who are thinking about receiving biological treatment should talk to their dermatologist about the advantages and disadvantages.
Lifestyle Changes and Alternative Solutions for Psoriasis
Lifestyle changes and alternative treatments, in addition to medical treatments, can help manage psoriasis symptoms. Here are some possibilities:
-
Maintain a healthy diet: There is no psoriasis diet, but eating a healthy and balanced diet may help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in fish and fish oil supplements, may also be beneficial.
-
Exercise: Regular exercise can aid in the reduction of inflammation and the overall improvement of health. However, avoid activities that may cause a flare-up or skin injury.
-
Stress management: Stress can cause or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, so it's critical to learn how to control it. Meditation, yoga, and other relaxation methods could be beneficial.
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
-
Moisturise: Keeping the skin moisturised can help reduce itching and scaling. Apply fragrance-free moisturisers immediately after bathing or showering.
-
Light therapy: To slow the growth of skin cells, phototherapy, or light therapy, uses ultraviolet light. The usual setting for this treatment is a medical office or clinic.
-
Natural remedies: Some natural treatments, like aloe vera, tea tree oil, and apple cider vinegar, may help lessen the symptoms of psoriasis. However, when using natural remedies, use caution because they may not be safe or effective for everyone. Before attempting to use any natural remedies, it is critical to consult with a healthcare professional.
It's important to remember that psoriasis, which is a chronic condition, currently has no treatment. However, symptoms can be lessened and life quality can be increased with the right management and treatment.
Stress Management and Psoriasis
In order to prevent psoriasis flare-ups, people with the condition should learn to control their stress. Exercise, meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and other relaxation practices are some helpful stress-management strategies. In addition, counselling or therapy may be beneficial for those who are under a lot of stress due to psoriasis or other conditions in their lives.
Psoriasis sufferers must also look after their general health by maintaining a good diet, getting adequate sleep, and abstaining from tobacco use and binge drinking. Some people with psoriasis may benefit from sun exposure, but it's crucial to protect the skin from sunburn and consult a dermatologist about the right quantity of sun exposure. Alternative therapies have been investigated as potential psoriasis treatments, including acupuncture, massage, and natural supplements, but additional studies are required to determine their efficacy. Before using any alternative treatments, it's crucial to discuss them with a dermatologist because some of them could interact negatively with prescription drugs or pose other dangers.
Dietary Changes and Supplements for Psoriasis
Some patients may find that making dietary modifications and taking supplements can help manage their psoriasis symptoms, but more research is required to know how beneficial these treatments are. According to some research, eating an anti-inflammatory diet like the Mediterranean diet or one high in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may help lessen the symptoms of psoriasis. Red meat, dairy products, and refined carbohydrates should all be avoided or consumed in moderation if they are known to cause inflammation.
Some supplements might also be anti-inflammatory, which may be advantageous for those who have psoriasis. Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and curcumin, the active component of turmeric, are a few of them. Before taking any supplements, you should consult your doctor because they may interfere with your prescription drugs or cause other unwanted side effects. Furthermore, while dietary changes and supplements may aid in the management of psoriasis symptoms, they should not be used in place of prescribed medical treatments.
Alternative Therapies and Their Effectiveness
Some people use a variety of alternative therapies to treat their psoriasis symptoms, despite the lack of strong scientific evidence for their efficacy. Some of these treatments consist of:
-
Acupuncture: A procedure in which the body's nerves, muscles, and connective tissue are stimulated by inserting tiny needles into predetermined body locations. The itching and other psoriasis symptoms are sometimes treated with acupuncture.
-
Aloe vera: A plant extract that has a reputation for being calming and restorative. Aloe vera gel can be topically applied to promote skin healing and reduce inflammation.
-
Dead Sea salt: It's thought that taking a bath in water containing dead sea salt will help to calm and moisturise psoriasis-affected skin.
-
Yoga and meditation: Mind-body exercises like meditation and yoga can help you control your stress levels, which is a common cause of psoriasis flare-ups.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids: These fats can be found in fish oil supplements and some foods, including salmon and walnuts, and they may help to lessen the inflammation that is linked to psoriasis.
-
Turmeric: A spice commonly used in Indian cuisine, turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with anti-inflammatory properties. Some people treat their psoriasis symptoms by applying turmeric topically or taking turmeric supplements.
It's important to understand that while some people may find relief from these alternative therapies, they shouldn't be used in place of medical care recommended by a healthcare professional. Before beginning any new treatments, it's also crucial to speak with a healthcare professional to make sure they're secure and efficient.
































