Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects approximately 125 million people worldwide. While both men and women can develop psoriasis, there are unique challenges and concerns that affect women living with this condition. In this blog, we will discuss the prevalence and nature of psoriasis in women, hormonal influences on psoriasis, coping with emotional and social challenges, managing psoriasis during pregnancy and postpartum, treatment options for psoriasis in women, lifestyle changes for managing psoriasis, and resources and support for women with psoriasis.
The Prevalence and Nature of Psoriasis in Women
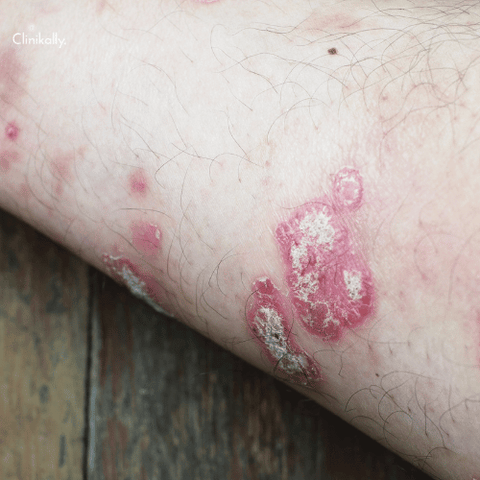
Psoriasis affects around 1-3% of the general population, and studies suggest that women are slightly more likely to develop psoriasis than men. The disease can occur at any age, but most commonly affects individuals between 15 and 35 years old. There are several types of psoriasis, with the most common form being plaque psoriasis. This type of psoriasis appears as raised, red, scaly patches on the skin. Women with psoriasis may also experience joint pain and stiffness, which can be a sign of psoriatic arthritis.
Female Hormonal Factors and Psoriasis
Hormonal changes in women can influence the severity of psoriasis symptoms. For example, some women may notice an increase in psoriasis flare-ups during their menstrual cycle, while others may experience relief during pregnancy. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also affect the severity of psoriasis symptoms, with some women experiencing improvement while others may see an increase in symptoms.
Coping with Psoriasis: Emotional and Social Challenges
Living with psoriasis can have a significant impact on a woman's emotional and social wellbeing. Women with psoriasis may experience low self-esteem, anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Coping with psoriasis involves managing both the physical and emotional aspects of the disease. Women with psoriasis can benefit from seeking support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals. Building a support network can help women manage the emotional and social challenges associated with the disease.
Psoriasis during Pregnancy and Postpartum
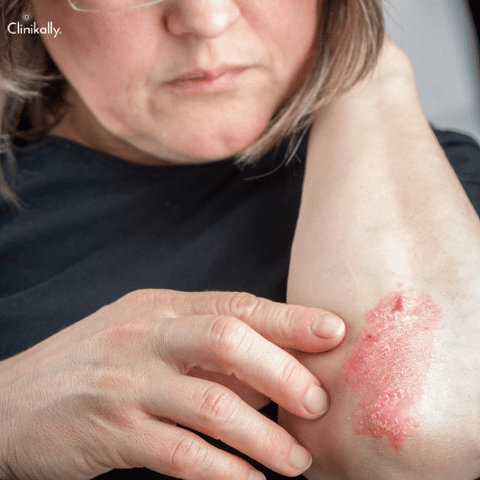
Pregnancy and postpartum can be challenging times for women with psoriasis. During pregnancy, psoriasis symptoms may improve for some women, while others may experience flare-ups. Similarly, after giving birth, some women may experience improvements in their psoriasis symptoms, while others may see a worsening of their condition. It is important for women with psoriasis who are pregnant or have recently given birth to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively.
Managing Psoriasis during Pregnancy
The treatment of psoriasis during pregnancy can be complex, as some medications may be harmful to the developing fetus. However, many women are able to safely manage their psoriasis symptoms during pregnancy with topical treatments and phototherapy. In some cases, systemic medications or biologic therapies may be recommended if the benefits outweigh the risks. Women with psoriasis who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should discuss their treatment options with their healthcare providers to ensure the best possible outcomes for themselves and their babies.
Psoriasis and Postpartum Recovery
After giving birth, women with psoriasis may experience changes in their skin and psoriasis symptoms. In some cases, psoriasis may improve, while in others, it may flare up. Breastfeeding can also affect psoriasis, as some medications used to treat the condition may not be safe for infants. Women with psoriasis who are breastfeeding should consult their healthcare providers about the best treatment options for themselves and their babies. Additionally, postpartum recovery can be challenging for women with psoriasis, both physically and emotionally. Building a support network and practicing self-care can help women manage the stresses of new motherhood while also managing their psoriasis symptoms.
Overall, women with psoriasis who are pregnant or have recently given birth may face unique challenges related to managing their condition. However, with the guidance of their healthcare providers and a supportive network, women can effectively manage their psoriasis symptoms and achieve optimal health outcomes.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis in Women

There are several treatment options available for women with psoriasis. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition, the location of the affected skin, and other individual factors. Some of the most common treatments for psoriasis in women include topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications, and biologic therapies.
Topical Treatments and Skincare
Topical treatments are medications that are applied directly to the skin. They can be effective for treating mild to moderate psoriasis and are often used as a first-line treatment. Topical treatments for psoriasis include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, retinoids, and coal tar preparations. In addition to medications, women with psoriasis can also benefit from developing a skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and avoiding triggers that can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
Phototherapy and Systemic Medications
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation and slow the growth of skin cells. This treatment is typically administered in a healthcare setting and can be effective for treating moderate to severe psoriasis. Systemic medications, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin, are prescription medications that can be effective for treating severe psoriasis. These medications work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation.
Biologic Therapies and Personalized Approaches
Biologic therapies are a newer class of medications that are designed to target specific parts of the immune system that are involved in psoriasis. Biologic therapies are administered through injections or infusions and can be effective for treating moderate to severe psoriasis. Personalized approaches to psoriasis treatment involve working closely with healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan that takes into account the patient's medical history, lifestyle factors, and treatment preferences. This approach can help women with psoriasis achieve the best possible outcomes and improve their quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Psoriasis

In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing psoriasis in women. Making changes in areas such as stress reduction, self-care, diet, exercise, and sleep hygiene can help reduce inflammation, prevent triggers, and improve overall health and well-being.
Stress Reduction and Self-Care
Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis, and reducing stress levels can help prevent flare-ups. Women with psoriasis can try a variety of stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or tai chi. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as spending time with loved ones or pursuing hobbies, can also help reduce stress levels.
Self-care is also important for managing psoriasis. Women with psoriasis should take time to care for their skin, including moisturizing regularly, avoiding harsh soaps or other irritants, and using sunscreen. They can also consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as aromatherapy, massage, or warm baths into their daily routine.
Diet, Exercise, and Sleep Hygiene
While there is no specific diet that has been proven to cure or prevent psoriasis, maintaining a healthy diet can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Women with psoriasis should consider incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, fatty fish, and nuts into their diet while avoiding processed foods, sugar, and alcohol.
Regular exercise can also help manage psoriasis by reducing stress levels, improving circulation, and promoting overall health. Women with psoriasis can engage in a variety of activities such as walking, swimming, yoga, or strength training.
Finally, good sleep hygiene is essential for managing psoriasis. Women with psoriasis should aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night and practice good sleep hygiene habits such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, avoiding electronic devices before bed, and creating a comfortable sleep environment.
Resources and Support for Women with Psoriasis

Women with psoriasis can benefit from seeking out resources and support to help manage the disease. National psoriasis organizations, such as the National Psoriasis Foundation in the United States, provide information and resources on psoriasis treatments, research, and support groups. Online forums and social media groups can also provide a sense of community and support for women living with psoriasis. Women with psoriasis should also work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets their individual needs and goals.
In conclusion, psoriasis can have a significant impact on women's health and wellbeing. Women with psoriasis may face unique challenges and concerns related to hormonal influences, emotional and social wellbeing, and managing the disease during pregnancy and postpartum. However, there are several treatment options, lifestyle changes, and resources available to help women manage their psoriasis symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. By working closely with healthcare providers and building a support network, women with psoriasis can achieve better health and wellbeing.
































