Skin pigmentation is a condition characterised by the darkening of a person's skin colour. It is caused by increased melanin pigmentation or the overproduction of melanin on the epidermis. Different factors, including exposure to sunlight, ageing and hormonal changes, can trigger hyperpigmentation. Identifying the different types of pigmentation on your face and skin is very important for getting rid of the same. In this blog, we will look more closely at types of pigmentation disorders, causes of pigmentation and how to get rid of pigmentation
What causes pigmentation on skin?

Skin with too much melanin is called hyperpigmented. Skin with too little melanin is called hypopigmented. Skin with no melanin is called depigmented. There can be several causes of skin pigmentation
Most common types of pigmentation disorders

There are several types of skin pigmentation, the most common ones are
-
Age spots
-
Melasma
-
Post inflammatory hyperpigmentation
|
Type |
Symptoms |
Where on body |
|
Age spots |
Brown, tan, or black spots that appear on the skin with sun overexposure |
Face or hands or on sun exposed areas of the body |
|
Melasma |
Large patches of darkened skin |
Generally, on the forehead, face, and stomach |
|
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation |
Spots or patches of darkened skin that appear after an inflammatory skin condition, such as acne or eczema |
Anywhere on the body |
Causes of hyperpigmentation
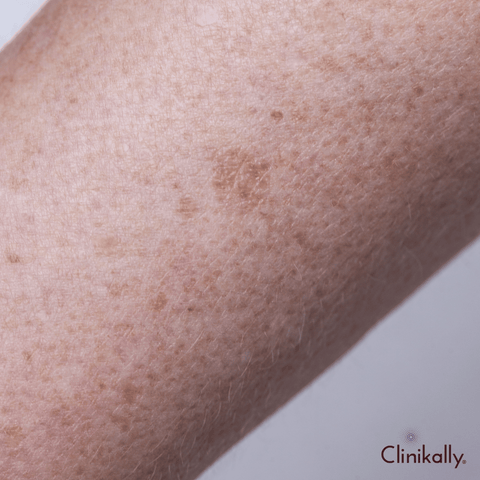
Hyperpigmentation occurs when some areas of the skin become darker than the surrounding skin due to an excess of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Hyperpigmentation has several causes and contributing factors, including:
-
Skin inflammation
-
Use of certain drugs, including minocycline, certain cancer chemotherapies, and use of birth control pills
-
Hormone system diseases like Addison's disease
-
Hemochromatosis (iron overload)
-
Sun exposure
-
Pregnancy (melasma, or mask of pregnancy)
-
Certain birthmarks
Causes of hypopigmentation

Hypopigmentation refers to areas of the skin that become lighter or lose their pigment. Some causes of hypopigmentation include:
-
Skin inflammation
-
Certain fungal infections (such as tinea versicolor)
-
Pityriasis alba
-
Certain medicines
-
A skin condition called idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis in sun-exposed areas such as the arms
-
Certain birthmarks
In case skin discolouration causes significant concern or there is persistent darkening or lightening it is best to consult a dermatologist who will correctly diagnose your condition and recommend creams, ointments, surgery, or phytotherapy based on your skin concern. At Clinikally, we provide online video consultation with best dermatologists in India who will give you a personalised treatment plan based on your specific skin concern.
Hyperpigmentation
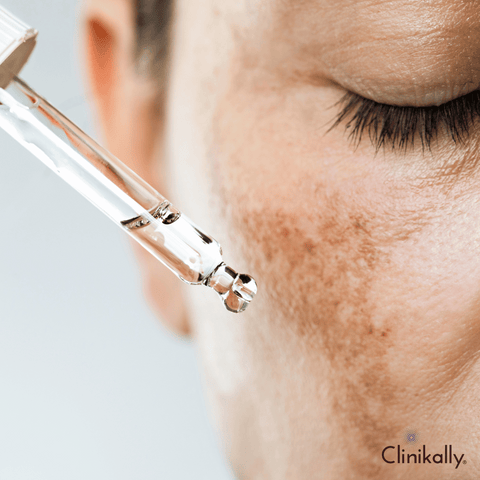

Normal skin contains cells called melanocytes. These cells are responsible for producing melanin. Melanin is what gives skin its color. Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that causes patches of darkened skin. It occurs when melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color, accumulates in one area and results in a darker-than-normal skin patch.
There are various types and causes of hyperpigmentation, including:
-
Sun Exposure: UV rays from the sun stimulate melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) to produce more melanin, resulting in sunspots, freckles, and general sun-induced hyperpigmentation.
-
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy (melasma or "mask of pregnancy"), menopause, or while taking birth control pills can cause an increase in melanin production in specific areas, resulting in dark patches.
-
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Following skin inflammation or injury from conditions such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, or cuts, the skin may produce excess melanin, resulting in dark spots or patches as part of the healing process.
-
Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as lentigines (age spots), post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and certain types of dermatitis, can result in localised skin darkening.
-
Genetic Factors: Some people are predisposed to hyperpigmentation due to genetics or family history.
-
Medications or Treatments: Certain medications, such as antimalarial drugs, antibiotics, hormone therapies, and chemotherapy, may cause increased skin pigmentation as a side effect.
-
Inflammatory Skin Conditions: Chronic inflammation from skin disorders such as lupus, lichen planus, or reactions to skin treatments can cause irregular pigmentation.
It's crucial to understand that various circumstances can cause hyperpigmentation, and the condition's intensity and appearance might vary. Treatment options vary according to the kind, origin, and extent of hyperpigmentation, and can range from topical creams and treatments to professional procedures such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or microneedling, all of which can help minimise or manage pigmentation irregularities. A dermatologist can advise you on the best course of action for your hyperpigmentation.
How to treat hyperpigmentation

Several treatments can help treat hyperpigmentation, including topical treatments like creams, moisturisers, and sunscreens, as well as cosmetic procedures like laser therapy or chemical peels. Natural remedies like aloe vera, licorice, and green tea extracts are also known to reduce the appearance of pigmentation on the skin.
Lifestyle changes to manage hyperpigmentation

Managing hyperpigmentation entails a combination of dietary adjustments, skincare regimens, and, in some cases, expert treatments. Here are some lifestyle changes that can help with hyperpigmentation management:
-
Sun Protection: To avoid further hyperpigmentation, protect your skin from the sun. Even on cloudy days, use sunscreen with a broad spectrum SPF of 30 or higher. When going outside, wear a hat, sunglasses, and seek shade.
-
Healthy Diet: Consume a healthy diet that is high in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Fruits and vegetables include antioxidants that can help fight free radicals, which cause skin damage.
-
Avoid Irritants: Hyperpigmentation can be exacerbated by some skincare products or environmental causes. Avoid harsh chemicals, perfumes, and known irritants. Before using new products extensively, patch them.
-
Gentle Skincare Routine: Use gentle skincare products that are appropriate for your skin type. Exfoliation that is too severe may aggravate hyperpigmentation. Choose products with skin-brightening chemicals such as niacinamide, vitamin C, or kojic acid.
-
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can have an effect on skin health. Practise stress-relieving techniques like meditation, yoga, or mindfulness to improve your overall well-being, which will benefit your skin.
-
Quit smoking: Smoking can cause skin damage and exacerbate hyperpigmentation. Quitting smoking can improve your skin's overall health.
-
Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration promotes skin health. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your skin hydrated.
-
Get Adequate Sleep: Sleep deprivation can have an impact on skin health and exacerbate skin problems. To assist skin regeneration, aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
-
Consult Professionals: Consider seeing dermatologists or skincare professionals for customised treatments and recommendations. In severe cases, they may recommend expert treatments such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or prescription drugs.
-
Be Patient: It takes time to manage hyperpigmentation. The importance of consistency in your skincare routine and lifestyle adjustments cannot be overstated. Results may not be apparent right away, so be patient and consistent in your efforts.
It's important to note that while lifestyle changes can help manage hyperpigmentation, some cases may require professional intervention. Consulting a dermatologist or skincare professional can provide personalised advice and treatment options suitable for your specific type of hyperpigmentation.
Over-the-counter vs. prescription treatments

The potency, efficacy, and specificity of over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications for skin disorders like hyperpigmentation vary. This is a comparison side by side:
Over-the-Counter Treatments:
-
Accessibility: OTC treatments are available without a prescription in drugstores, supermarkets, and online. They typically include serums, creams, lotions, and masks.
-
Ingredients: OTC products frequently have lower amounts of active chemicals. Kojic acid, glycolic acid, licorice extract, vitamin C, and niacinamide are common hyperpigmentation components available in over-the-counter remedies. While some chemicals have the potential to be useful, their concentrations may be lower than in prescription medications.
-
Effectiveness: OTC therapies for mild to moderate hyperpigmentation can be useful. They may help to enhance general skin tone, lessen the appearance of dark spots, and brighten the skin. However, when compared to prescription therapies, outcomes may take longer to occur.
-
Safety: OTC products have generally been tested for safety and are regarded safe when used according to the directions. They may not, however, be as beneficial for severe or persistent hyperpigmentation.
Prescription Treatments:
-
Potency: Prescription drugs have bigger concentrations of active ingredients and may be more potent. Dermatologists can prescribe stronger formulations such as hydroquinone, tretinoin (retinoids), corticosteroids, or combination creams that are not available over-the-counter.
-
Effectiveness: Prescription therapies are frequently more successful for mild to severe cases of hyperpigmentation. When compared to OTC products, they can target deeper layers of the skin and produce faster effects. They may, however, have a higher risk of side effects and should be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
-
Medical Supervision: Because prescription treatments are more potent, they must be administered under the supervision of a dermatologist or other healthcare expert. To monitor progress and handle any potential adverse effects, regular check-ups and follow-ups are required.
-
Cost: Prescription medications may be more expensive than over-the-counter medications, especially if insurance coverage is not available. However, for some people living with persistent hyperpigmentation, their efficacy and specialised approach may justify the greater expense.
When considering hyperpigmentation treatment options, it's important to consider the severity of the condition, skin sensitivity, potential side effects, and individual skin response. Consulting with a dermatologist or healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and skin type.
Melasma
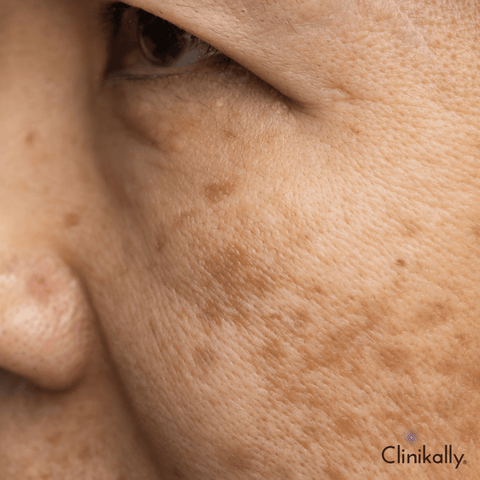
Melasma, also called the mask of pregnancy, is a common skin pigmentation disorder that results in skin discolouration. It can be found on the cheeks, upper lip and forehead. Melasma is caused by sun exposure or hormonal changes that cause an increase in melanin production by melanocytes. Melanin is the pigment that gives your skin its colour. If you have increased levels of melanin, your skin will appear darker than usual.
Causes of melasma

Melasma is caused by increased melanin (pigment) in your skin cells. It can occur due to pregnancy, hormonal changes, and sun exposure. When this happens, the result is brown or grey patches on your face. The condition often appears on the forehead, cheeks and nose, but it can also affect other body parts. This disorder is more common among women than men, especially during pregnancy or after giving birth. Dark-skinned individuals are also more susceptible to melasma than lighter-skinned people.
How to treat melasma
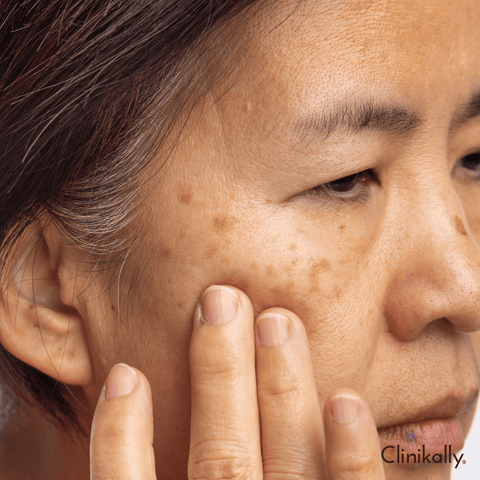
Melasma is usually treated with a combination of creams and lotions that contain prescription-strength hydroquinone or corticosteroids. These medications slow down melanin production in your body, so your skin will gradually lighten up over time. These products need to be monitored closely by your doctor since they have side effects such as dryness, peeling, and irritation.
Sun protection strategies for melasma

Melasma is a skin disorder characterised by darker patches of skin, typically on the face, that are frequently caused or exacerbated by sun exposure. Sunscreen is essential in the treatment of melasma. Here are some effective melasma sun protection methods:
-
Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher that offers UVA and UVB protection. Physical sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide may provide improved melasma protection.
-
Frequent Reapplication: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially if you're going to be outside or doing activities that may result in perspiration or water exposure; sunscreen should also be reapplied after swimming or excessive sweating.
-
Sun-Protective Clothing: To protect your face and skin from direct sunlight, use wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and clothing with adequate covering. Fabrics that are dark in color and densely woven provide superior protection.
-
Seek Shade: Seek shade whenever possible, especially during high sun hours (typically from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). Direct sun exposure should be limited to help prevent melasma from intensifying.
-
Use Sunshades or Umbrellas: To create shade and reduce direct sun exposure on your face when you are outside, bring along a portable umbrella or make use of sunshades.
-
Steer clear of Reflective Surfaces: Surfaces that reflect light, such as snow, sand, or water, can amplify UV rays. When near these surfaces, exercise extra caution and diligence in protecting yourself from the sun.
-
Consider Window Exposure: UV radiation can pass through windows. Consider using UV-protective window films or window coverings, especially if you spend a lot of time near windows.
-
Skincare Products in Your Routine: Include melasma-management skincare products in your routine. Ingredients like niacinamide, vitamin C, and licorice extract may help brighten and even out skin tone. However, these should be used in conjunction with, not in place of, sun protection.
-
Consult a Dermatologist: Consult a dermatologist if your melasma is persistent or severe. They can offer professional advice and may suggest treatments such as prescription-strength topical medications, chemical peels, or laser therapy that are tailored to your specific needs.
Sun protection methods must be consistent to effectively manage melasma. These techniques not only serve to avoid additional darkening of existing pigmentation, but they also help to maintain a more even skin tone and lower the likelihood of melasma flare-ups caused by sun exposure.
Expert tips to prevent pigmentation
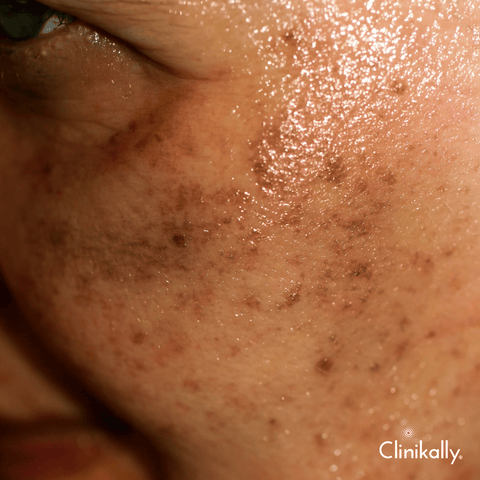
Pigmentation can be avoided through a combination of protective measures, skincare practises, and lifestyle choices. Here are some expert tips to help you avoid pigmentation issues:
-
Sun protection is essential: Apply sunscreen to your skin daily to protect it from harmful UV rays. Even on cloudy days, apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours, more frequently if you are outside or sweating.
-
Sun-Protective Clothing: Wear sun-protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and clothing that covers exposed areas. Dark-colored, tightly woven fabrics offer better protection.
-
Seek Shade: Limit direct sun exposure, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. When you are outside, look for shade or make your own with umbrellas or sunshades.
-
Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds and prolonged exposure to artificial UV radiation can cause skin damage and pigmentation problems.
-
Gentle Skincare Routine: Adopt a skincare routine that focuses on gentle cleansing and includes products containing antioxidants (vitamin C), niacinamide, and retinoids, which can help maintain skin health and even out skin tone.
-
Exfoliation Caution: Avoid harsh exfoliation, which can irritate the skin and possibly worsen pigmentation. Choose gentle exfoliation methods that are appropriate for your skin type.
-
Manage Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes caused by pregnancy or birth control can cause pigmentation changes such as melasma. Consult a healthcare professional for advice on how to manage hormonal fluctuations.
-
Address Skin Sensitivities: People with sensitive skin are more prone to pigmentation problems. To avoid skin irritation, use fragrance-free and hypoallergenic skincare products.
-
Healthy Lifestyle Practises: To maintain a healthy lifestyle, avoid smoking and binge drinking, eat a balanced diet high in vitamins and antioxidants, get enough sleep, manage stress, and stay hydrated.
-
Frequent Skin Checks: Examine your skin regularly to keep an eye out for any changes, such as newly formed moles or pigmented areas that do not seem right. Consult a specialist if you observe any worrying changes.
-
Speak with a Dermatologist: See a dermatologist if you are worried about pigmentation or have noticed any changes to your skin. They can offer tailored guidance and suggest appropriate skincare items, regimens, or methods to deal with pigmentation concerns.
Remember that pigmentation prevention necessitates consistent sun protection, a gentle skincare routine, and being aware of potential triggers. To effectively prevent pigmentation issues, tailor your skincare regimen and lifestyle habits to your skin type and specific concerns.
Daily skincare routine to prevent pigmentation

A daily skincare routine designed to prevent pigmentation should emphasise gentle yet effective practises that prioritise sun protection and skin health. Here's an example of a skincare routine:
Morning Routine:
-
Cleanser: Begin your day with a gentle cleanser that is appropriate for your skin type. Cleansing removes impurities from the skin without stripping it of its natural oils.
-
Toner (Optional): If desired, use a gentle, alcohol-free toner. Toners can help balance the pH of the skin and prepare it for subsequent products.
-
Vitamin C Serum: Apply a vitamin C serum to your skin. Vitamin C functions as an antioxidant, aids in skin brightening, and provides some protection against environmental damage.
-
Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Choose a sunscreen that is suitable for your skin type and offers UVA and UVB protection. If exposed to the sun, reapply every 2 hours.
Evening Routine:
-
Makeup Removal and Cleansing: Remove makeup thoroughly and cleanse your face to eliminate dirt, pollutants, and excess oil accumulated throughout the day.
-
Exfoliation (1-3 times per week): To slough off dead skin cells, use a gentle exfoliant suitable for your skin type. Scrubbing should be gentle, especially if you have sensitive skin.
-
Treatment Products: Use any treatment products that address your concerns, such as serums containing ingredients like niacinamide or retinoids, which are known for brightening and evening out the skin.
-
Moisturiser: Apply a hydrating and nourishing moisturiser to your skin type. Hydrated skin helps to maintain its barrier function and can help to prevent dryness, which can aggravate pigmentation issues.
-
Eye Cream (Optional): Apply an eye cream gently around the eye area to hydrate and protect delicate skin.
-
Night Cream or Retinol (Optional): Use an antioxidant-rich night cream or a retinol product appropriate for your skin. Retinol can help reduce pigmentation and improve skin texture by increasing skin cell turnover.
Additional Tips:
-
The secret is to be consistent: for best results, follow your skincare regimen every day.
-
Patch Test New Products: To ensure there are no negative reactions, test new products on a small area of your body before introducing them into your regular regimen.
-
Nutrition and Hydration: For general skin health, consume a diet high in vitamins and antioxidants and stay properly hydrated.
-
Professional Advice: If you have particular concerns about pigmentation or skin sensitivities, you might want to see a dermatologist for individualised recommendations.
Adjust this regimen to your skin's particular requirements, and keep in mind that the best way to manage pigmentation is through prevention. Regular sun protection and a gentle skincare routine can help prevent and minimise pigmentation issues over time.
Importance of vitamin C in pigmentation prevention

Because of its antioxidant qualities and capacity to inhibit melanin formation, the pigment responsible for dark spots and uneven skin tone, vitamin C plays an important role in pigmentation prevention and control. Here are some of the reasons why vitamin C is crucial for pigmentation prevention:
-
Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that aids in the neutralisation of free radicals produced by environmental stressors such as UV rays, pollution, and oxidative stress. Free radicals can contribute to skin damage and trigger pigmentation issues.
-
Inhibition of Tyrosinase Activity: Tyrosinase is an enzyme that is required for melanin synthesis in the skin. Vitamin C suppresses the activity of this enzyme, which reduces melanin production and prevents the creation of dark patches and hyperpigmentation.
-
Brightening and Evening Skin Tone: Vitamin C has skin-brightening properties that promote a more even complexion by fading existing dark spots and pigmentation. Continuous vitamin C use can result in a more radiant and uniform skin tone.
-
Collagen Synthesis: Vitamin C is required for collagen synthesis, which helps to maintain skin firmness and elasticity. Improving skin texture can help to reduce the visibility of pigmentation irregularities.
-
Sun Protection: While not a substitute for sunscreen, vitamin C can provide an extra layer of protection against UV-induced skin damage. It does not replace the need for sunscreen, but it can be used in conjunction with it.
-
Repair and regeneration: Vitamin C promotes the regeneration of healthy skin cells and may help restore damaged skin caused by pigmentation disorders.
Vitamin C serums and creams added to a skincare regimen can help prevent and treat pigmentation disorders. However, while vitamin C is helpful, its effects may vary depending on the concentration, formulation, and frequency of administration. To achieve the best results in pigmentation prevention, apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen every day, practise sun protection measures, and combine vitamin C with additional complementing substances such as sunscreen, niacinamide, or other skin-brightening agents. A dermatologist or skincare specialist can assist you in determining the best vitamin C supplement or regimen for your skin type and specific pigmentation concerns.
Get rid of pigmentation on skin!

Skin pigmentation can be managed or reduced with continuous skincare routines, preventative measures, and, in some situations, expert treatments. Sun protection, skincare products (such as vitamin C, niacinamide, and hydroquinon), exfoliation, professional treatments (such as chemical peels, laser therapy, and microneedling), avoiding irritants, consulting a dermatologist, and patience are all actions you may take to help reduce pigmentation. It's critical to remember that everyone's skin reacts differently to treatments. To discover the most effective treatment strategy for you, tailor your skincare regimen to your skin type, be patient with the process, and seek professional guidance if you have recurrent pigmentation issues.
Natural remedies for skin pigmentation

Natural therapies may be beneficial in the treatment of skin pigmentation. While they will not completely eradicate pigmentation, they will assist to reduce its appearance and prevent further darkening. Here are a few natural cures that people frequently use:
-
Aloe Vera: Aloe vera offers moisturising and calming effects. Direct use of pure aloe vera gel to pigmented areas may help soothe the skin and maybe lighten dark patches over time.
-
Lemon Juice: Citric acid, found in lemon juice, has natural bleaching effects. As a natural lightening agent, diluted lemon juice can be applied to dark patches. However, lemon juice can be irritating to some skin types, so perform a patch test and follow up with sunscreen to avoid sun sensitivity.
-
Turmeric: Turmeric is anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant. As a mask, apply a paste comprised of turmeric powder and a suitable base (such as yoghurt or honey) to the affected regions. Over time, it may assist in lightening the skin.
-
Apple Cider Vinegar: Acetic acid in apple cider vinegar may help brighten black stains. Apply apple cider vinegar to the skin with a cotton ball after diluting it with water. To avoid skin irritation, it is critical to patch-test and dilute it adequately.
-
Green Tea Extract: Green tea contains antioxidants that may aid in the reduction of pigmentation and the calming of the skin. Topically applying cool green tea bags or green tea extract can provide some benefits.
-
Milk or Yogurt: Lactic acid in milk or yoghurt has mild exfoliating capabilities that may aid in skin lightening. Apply a tiny amount of milk or yoghurt to the afflicted regions and allow for a few minutes before rinsing.
-
Honey: Honey contains antimicrobial and moisturising effects. It can be blended with other substances such as lemon juice or aloe vera to make a soothing mask for sunburned skin.
It's important to realise that natural therapies may not be as effective as medical treatments and that results may vary widely across individuals. In addition, some natural ingredients can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some persons. Before beginning any natural therapy, perform a patch test to check for adverse reactions, and discontinue use if discomfort or pain occurs. Consistency and patience are required while using natural treatments. A dermatologist consultation is indicated for persistent or severe pigmentation disorders to explore more effective and precise treatment choices that are appropriate for your skin type and concerns.
Advanced dermatological treatments for pigmentation
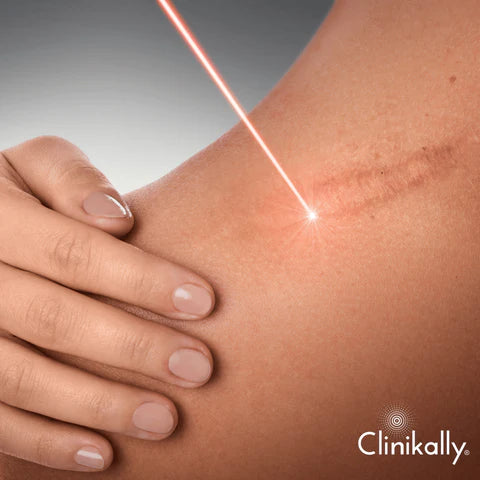
Advanced pigmentation dermatological treatments include a variety of procedures and therapies that are specially designed to target and diminish hyperpigmentation, providing more potent and focused solutions than over-the-counter medicines. Here are some sophisticated treatments that dermatologists regularly use:
-
Chemical Peels: To exfoliate the skin's top layers, dermatologists utilise chemical peels containing various acids (such as glycolic acid, salicylic acid, or trichloroacetic acid). This aids in the reduction of pigmentation, the improvement of skin texture, and the promotion of even skin tone.
-
Laser Therapy: Laser treatments that target pigmented areas, such as fractional laser, intense pulsed light (IPL), or Q-switched lasers, break down excess melanin and stimulate collagen formation. Laser therapy has been shown to successfully remove pigmentation and enhance skin texture.
-
Microneedling: This process involves the use of a device with fine needles to create regulated micro-injuries in the skin, which stimulates collagen synthesis and aids in the improvement of pigmentation abnormalities.
-
Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves freezing and destroying pigmented regions with liquid nitrogen. It's typically used to treat specific types of pigmentation, such as moles or tiny patches.
-
Topical Prescription Medications: A skin-lightening chemical of prescription strength that suppresses melanin formation and helps erase dark spots. Prescription retinoids, such as tretinoin or adapalene, promote skin cell turnover, resulting in more even skin tone and less pigmentation.
-
Microdermabrasion: This process exfoliates the skin's outer layer with a device that has a diamond-tipped or abrasive surface, which helps to reduce pigmentation abnormalities.
-
Cosmetic Procedures: To effectively address specific pigmentation disorders, dermatologists may offer customised combination treatments, such as combining chemical peels with laser therapy or other modalities.
Because these complex treatments necessitate specialised equipment and experience, they should only be conducted by skilled specialists. Consult with a dermatologist or skincare specialist before undergoing any advanced dermatological therapy to establish the best technique or combination of treatments for your skin type, specific pigmentation concerns, and general skin health. Furthermore, it is critical to carefully follow post-treatment care instructions and to wear sun protection regularly, as UV exposure can cause or exacerbate pigmentation disorders.
































