Face acids, also known as chemical exfoliants, are popular skincare products that can improve the texture and appearance of your skin. Face acids are classified into two types: alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs). AHAs work on the skin's surface and are water-soluble, whereas BHAs are oil-soluble and penetrate deeper into the pores.
Here's a beginner's guide to using face acids for skincare:
-
Start with a low concentration: If you're new to face acids, start with a low-concentration product to avoid irritation. Typically, 5-10% is a good starting point.
-
Patch test: Before using face acid all over your face, patch test a small area to make sure your skin doesn't react negatively to it.
-
Choose the suitable acid for your skin type: AHAs like glycolic acid are great for dry and sun-damaged skin, while BHAs like salicylic acid are better for oily and acne prone skin.
-
Use once or twice a week: Don't overdo it with face acids. Start by using them once or twice a week and gradually increase as your skin adjusts.
-
Follow with sunscreen: Face acids can increase your skin's sensitivity to the sun, so always follow up with sunscreen to protect your skin.
-
Moisturize: After using face acid, it's important to moisturize to help soothe and hydrate the skin.
-
Don't combine with other exfoliants: Avoid using other physical exfoliants like scrubs or brushes on the same day you use a face acid. This can be too harsh on your skin.
-
Be patient: It can take time to see the benefits of using face acid. Don't expect overnight results and be consistent with your use.
What are skincare acids?

Skincare acids are chemical elements that exfoliate, brighten, and improve skin texture. They are present in many skincare products. There are many different kinds of skincare acids, each with a unique set of advantages and qualities. Some common types of skincare acids include
-
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): AHAs are water-soluble acids derived from sugars found in fruits and milk. They work by removing the top layer of dead skin cells from the skin's surface, revealing smoother, brighter skin beneath. AHAs are commonly found in glycolic acid, lactic acid, and mandelic acid.
-
Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs): BHAs are oil-soluble acids that work well for unclogging pores and treat acne-prone skin. Salicylic acid is the most widely used BHA in skincare.
-
Polyhydroxy Acids (PHAs): PHAs are a newer type of acid that is similar to AHAs but has larger molecules that do not penetrate as deeply into the skin. As a result, they are a gentler option for those with sensitive skin. PHAs include gluconolactone and Lactobionic acid.
-
Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C): Ascorbic acid is a water-soluble vitamin that is a powerful antioxidant and aids in skin brightening, hyperpigmentation reduction, and collagen production.
-
Hyaluronic Acid: Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring molecule that aids in the retention of moisture in the skin. It is frequently used in skincare products to hydrate and plump the skin.
-
Retinoids: Retinoids are a type of Vitamin A that promotes cell turnover, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and improves skin texture. Retinoids are available in both prescription and over-the-counter dosages.
Azelaic acid

Azelaic acid is a prescription medication used to treat acne and rosacea. It is an organic dicarboxylic acid with keratolytic, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties. Azelaic acid functions by eradicating acne-causing bacteria, reducing swelling, and assisting in pore unclogging.
Azelaic acid can be applied to the face and other affected areas of the body as a topical cream, gel, or foam. It is typically applied twice daily, and acne can be improved in as little as four weeks. It can be combined with other acne medications like benzoyl peroxide or retinoids. Azelaic acid has also been shown to help with hyperpigmentation by reducing the production of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
Ellagic acid

Ellagic acid is a polyphenol compound found in plants such as strawberries, raspberries, pomegranates, and some nuts. Its potential health benefits, particularly as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, have been investigated. This approach may also help to lower the body's oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which have been linked to the development of chronic illnesses like diabetes and heart disease.
Ellagic acid is a dietary supplement, but it's usually advised to get it from whole foods as part of a balanced diet rather than just from supplements. As with any supplement, talk to your doctor before taking ellagic acid, especially if you are taking medication or have a pre-existing medical condition.
Ferulic acid
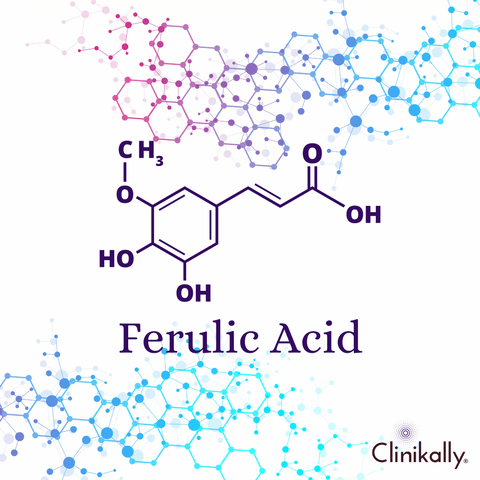
Ferulic acid is a type of phenolic acid, which is a class of compounds found in many plants. It is a naturally occurring antioxidant found in a variety of fruits and vegetables, including oranges, rice, wheat, and oats. Ferulic acid may have a number of health benefits, including the ability to reduce inflammation, protect against oxidative stress, and promote healthy ageing. Because of its antioxidant properties, it is also used in a variety of skincare and cosmetic products to help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Glycolic acid

Glycolic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) commonly found in skincare products. It is made from sugar cane and has the smallest molecular size of all the AHAs, which enables it to penetrate the skin effectively and deeply. Glycolic acid is commonly used as an exfoliant because it can help remove dead skin cells from the skin's surface and promote cell turnover. This can help to improve skin texture and tone while also reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. It can aid in boosting skin moisture levels and promoting collagen production, which can enhance the general look and health of the skin. It is important to note, however, that glycolic acid can be irritating to some people, particularly those with sensitive skin.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is a polysaccharide that occurs naturally in the human body. It is a significant element of the extracellular matrix, which is found in many tissues, including skin, cartilage, and synovial fluid. Hyaluronic acid is a glycosaminoglycan, which is a carbohydrate made up of repeating units of disaccharides. Hyaluronic acid plays many crucial biological roles, including promoting tissue repair, maintaining skin hydration, and lubricating joints. Because of its ability to retain moisture, hyaluronic acid has become a popular ingredient in many skincare products. It is believed to hydrate and plump the skin, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Kojic acid

The cosmetic and skincare industries frequently employ the natural substance kojic acid. It is derived from various fungi and is frequently used in skin-lightening and brightening products due to its reputation for preventing the skin's melanin from being produced. Kojic acid works by blocking an enzyme called tyrosinase, which is necessary for the production of melanin in the skin. By blocking this enzyme, kojic acid can help to reduce the appearance of dark spots, hyperpigmentation, and other forms of skin discoloration. It's important to note that kojic acid can cause skin irritation and sensitivity in some people, so always patch-test kojic acid products before using them on larger areas of the skin.
Lactic acid

Lactic acid is a chemical compound with the formula C3H6O3. It is a carboxylic acid produced by the body during certain metabolic processes, such as the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration). Bacteria also produce lactic acid during the fermentation of certain foods, such as yoghurt, cheese, and sauerkraut. Lactic acid is produced in the body by muscles during intense exercise or when the body is stressed. This can result in lactic acid build-up in the muscles, resulting in muscle fatigue, soreness, and cramping.
Mandelic acid

Mandelic acid has the chemical formula C8H8O3 and is an organic acid. It is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) that is used in a variety of skincare products because of its ability to exfoliate and improve skin texture and appearance. The bitter almond extract was used as the source for the discovery of Mandelic acid in 1831 by German chemist Justus von Liebig. It is a crystalline solid that is water, alcohol, and ether soluble.
Mandelic acid is used to treat acne and other skin conditions because of its antibacterial properties. In addition, it is employed in the synthesis of numerous pharmaceuticals and the production of plastics, resins, and other industrial goods.
Phytic acid

Many plant-based foods, especially seeds, grains, and legumes, contain phytic acid, also known as inositol hexaphosphate (IP6). It is the primary storage form of phosphorus in plants. The unique structure of phytic acid allows it to bind to certain minerals, including calcium, iron, and zinc, reducing their bioavailability. Thus, phytic acid-containing foods may cause mineral deficiency, and they also have some potential health benefits.
Traditional food preparation techniques like soaking, sprouting, and fermentation can lower a food's phytic acid content, allowing the body to more easily absorb the minerals it contains. Overall, while phytic acid can interfere with mineral absorption, it can also have health benefits and can be managed with proper food preparation and dietary choices.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is an organic acid that is commonly found in a wide range of skincare and pharmaceutical products. It is derived from willow bark and other plants and has been used for centuries for its anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties. Salicylic acid is commonly used as an exfoliant in skin care to help remove dead skin cells and unclog pores, making it a popular ingredient in acne treatments. It can also help to reduce inflammation and redness, making it an excellent ingredient for people who have sensitive or acne-prone skin.
Salicylic acid is used to treat a variety of conditions in medicine, including acne, psoriasis, warts, and dandruff. It works by allowing the medication to penetrate deeper into the affected area by breaking down the outer layer of skin cells. Salicylic acid comes in a variety of forms, including creams, lotions, gels, and shampoos.
Which acid suits my skin type?

Choosing the right acid for your skin type depends on your individual skin concerns and sensitivities. Here are some general guidelines for common skin types:
-
Oily or acne-prone skin: Salicylic acid is often recommended for those with oily or acne-prone skin. It can penetrate the pores to remove excess oil and help unclog them, which can help prevent breakouts.
-
Dry or sensitive skin: If you have dry or sensitive skin, you may want to avoid strong acids like glycolic acid or lactic acid, as they can be too harsh and potentially irritating. Instead, you may want to try a milder acid like mandelic acid, which can exfoliate the skin without causing irritation.
-
Normal or combination skin: If you have normal or combination skin, you may benefit from using a combination of different acids. For example, you could use glycolic acid to help brighten and exfoliate the skin, and hyaluronic acid to provide hydration.
Before applying an acid to your entire face, start with a lower concentration and patch-test it on a small area of your skin. If you're unsure about which acid to use, always consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional.
Face acid for skin whitening

Acids, such as hydroxy acids or glycolic acids, can be used in a skincare routine to exfoliate and improve skin texture and appearance, but they should be used with caution and under the supervision of a licensed dermatologist or skincare professional. It is important to note that the amount and type of pigment (melanin) in the skin determines skin color, and using acid to whiten the skin can be dangerous and cause harm to the skin, including irritation, inflammation, and even scarring. Furthermore, attempting to lighten the skin in this manner can perpetuate harmful and discriminatory beauty standards that favor lighter skin tones over darker skin tones.
Face acid for hyperpigmentation

It is not advised to use face acid for hyperpigmentation without first consulting a dermatologist. Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that occurs when the skin produces an excessive amount of melanin, resulting in dark spots and uneven skin tone. Face acids that can be used to treat hyperpigmentation include alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid and lactic acid, as well as beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) like salicylic acid. These acids exfoliate the skin's top layers and promote cell turnover, which can help fade hyperpigmentation over time. However, it's important to note that these acids can be harsh on the skin and can cause irritation, redness, and sensitivity. To avoid damaging your skin, choose the right concentration and apply the acid correctly.
Face acid for acne

There are several types of facial acids that can be helpful in treating acne:
-
Salicylic acid: This beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) is a popular ingredient in acne treatments because it can penetrate deep into the pores and exfoliate the skin. It can also reduce inflammation and redness.
-
Glycolic acid: This alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) can help exfoliate the skin and reduce the appearance of acne scars. It can also improve skin texture and tone.
-
Lactic acid: This AHA can help exfoliate the skin and reduce the appearance of acne scars. It can also improve skin hydration.
-
Mandelic acid: This AHA is a gentler exfoliant than glycolic or lactic acid, making it a good option for people with sensitive skin. It can also help reduce inflammation and redness.
Takeaway: What to keep in mind when using acids for skin care

Acids is a popular ingredient in many skincare products because they can help to exfoliate, brighten, and even out the skin. However, there are some things to keep in mind when using acids for skincare to avoid potential skin damage or irritation.
-
Know your skin type: Different acids work best for different skin types. For example, those with sensitive skin may want to avoid strong acids like glycolic or salicylic acid and opt for gentler options like lactic or mandelic acid.
-
Start slow: When using acid for the first time, start with a low concentration and apply it only once or twice a week. Gradually increase frequency and concentration as your skin gets used to it.
-
Always use sunscreen: Acids can make your skin more sensitive to the sun, so it's important to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every day.
-
Don't mix and match: Avoid using multiple acidic products at the same time, as this can lead to irritation or even chemical burns. Stick to one acid at a time and allow your skin to adjust before introducing another.
-
Avoid using acids around the eye area: The skin around the eyes is more delicate and sensitive, so it's best to avoid using acids in that area to prevent irritation or damage.
-
Moisturize: Acids can be drying to the skin, so it's important to use a hydrating moisturizer after applying an acid.
-
Consult a professional: If you're unsure about which acids to use or how to use them properly, it's a good idea to consult a dermatologist or skincare professional for guidance.
By keeping these things in mind, you can incorporate acids into your skincare routine safely and effectively and reap the benefits they provide.

































2 comments
Buli
Very informative. I struggle with hyperpigmentation a lot
Thanks
Very informative. I struggle with hyperpigmentation a lot
Thanks
jaspreet kaur
Hello i am cossmetologist ..this website is awesome there notes are very good
Hello i am cossmetologist ..this website is awesome there notes are very good